Parallels RAS Front-End Load Balancing Using Microsoft Azure Load Balancer
This guide shows the step-by-step configuration for deploying Microsoft Azure Load Balancer to front-end load balancing for a Parallels® Remote Application Server (RAS) environment deployed on Microsoft Azure on Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
Note: It is assumed that the reader has a basic understanding of both Microsoft Azure and Parallels RAS. This guide will only focus on the configuration of the Microsoft Azure Load Balancer and Parallels Secure Client Gateway load balancing.
Get more information about Parallels RAS.
Pre-Requisites and Assumptions
The below is a list of pre-requisites and assumptions that were noted prior to deploying the Microsoft Azure Load Balancer.
- Parallels RAS core infrastructure components—such as Parallels RAS Publishing Agent and RD Session Host—have been created.
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Network Design and Configuration has been carried out.
- The required Parallels RAS ports are to be opened both from the Azure Network Security Groups (NSG) and the Windows firewall on the virtual machines (VMs) in question.
This guide focuses on the Basic load balancer configuration, not the Standard. However, both are supported to load balance front-end traffic to a Parallels RAS infrastructure.
Document Process Flow
Following the high-level logical design shown in the next section, this document will take the reader through the following process to complete Azure Load Balancer configuration with Parallels RAS Secure Client Gateways:
- Create an Availability Set
- Create VMs as Part of the Availability Set
- Create Azure Load Balancer
- Create a Back-End Pool
- Create Health Probe
- Create Load Balancing Rules
- Test and Evaluate Load Balancing
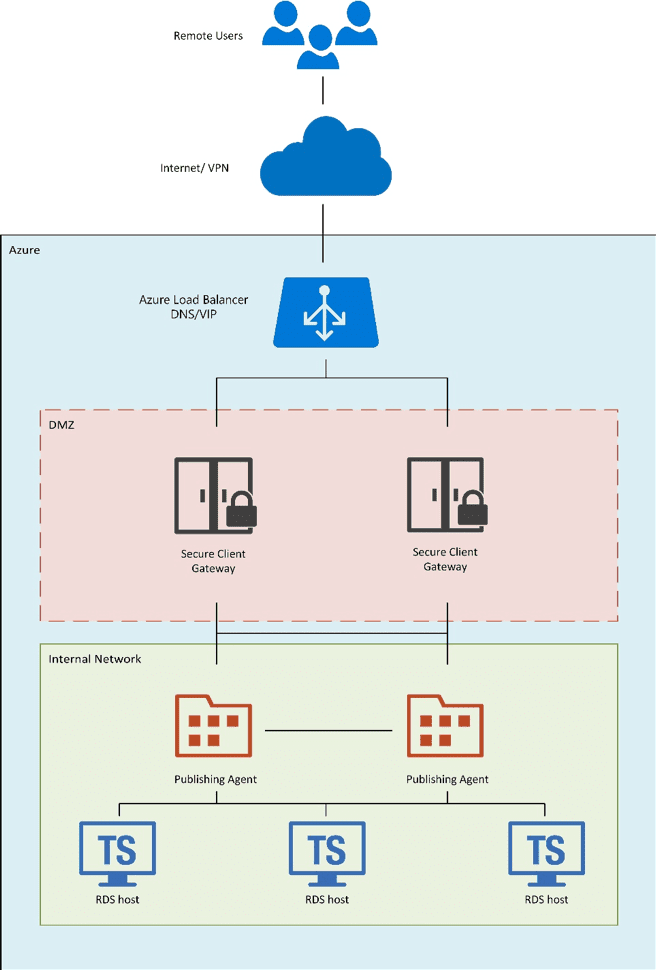
High-Level Logical Diagram
The following high-level logical diagram shows a load-balanced endpoint for external traffic that is shared and load balanced among two instances acting as Parallels RAS Secure Client Gateways, which are set up in high availability and located in a segregated secured network (DMZ).
Step 1 – Create an Availability Set
Prior to deploying Parallels RAS Secure Client Gateway servers on Microsoft Azure as IaaS, it is important to create an availability set.
An availability set is a logical grouping capability that you can use in Azure to ensure that the VM resources you place within it are isolated from each other when they are deployed within an Azure datacenter. Azure ensures that the VMs you place within an availability set run across multiple physical servers, compute racks, storage units, and network switches.
Using availability sets will increase the availability and reliability of your Parallels RAS Secure Client Gateways (SCG). It is required if you are planning to load balance front-end traffic from the Azure LB to more than one VM that will host the Parallels RAS SCG.
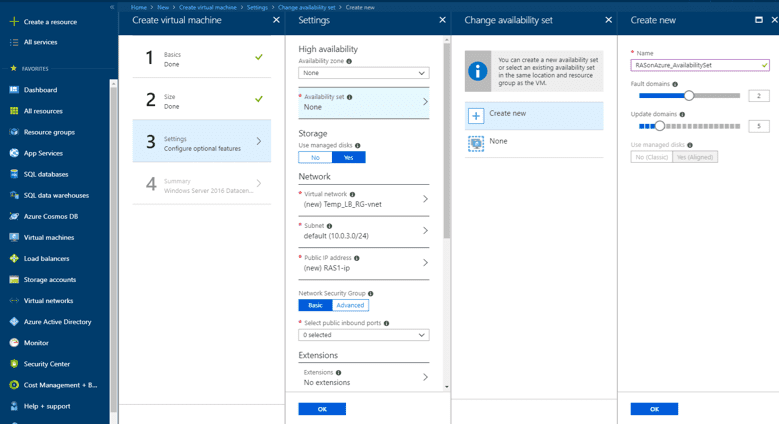
In this guide, we illustrate the creation of an availability set as part of the creation of a VM itself via the Azure portal.
- Under Settings > Configure optional features, choose Availability set and choose Create New.
- Set the name of the set.
- Choose Fault Domain to define the group of VMs that share a common power source and network switch.
- Choose Update Domain to indicate groups of VMs and underlying physical hardware that can be rebooted at the same time.
See more information about Fault Domain and Update Domain.
Microsoft Tip: To provide redundancy to your application, we recommend that you group two or more VMs in an availability set. This configuration ensures that during a planned or unplanned maintenance event, at least one VM will be available and meet the 99.95% Azure SLA.
See other methods for creating an availability set.
Important to note:
- A VM can only be added to an availability set when it is created.
- The availability set of a VM can’t be changed after it is created.
- You need to delete and then recreate the VM if need to change the availability set after the VM creation.
Step 2 – Complete VMs’ Creation and Parallels RAS SCG Installation
Complete the creation of VMs that are planned to host the Parallels RAS SCG. This can be easily carried out from the Azure Portal VM creation wizards. See a quick guide.
Once VMs are created, you can go ahead with the Parallels RAS SCG installation and configuration. For more information on Parallels RAS SCG installation, see the Parallels RAS Administration Guide.
Step 3 – Create Azure Load Balancer
Once the VMs have been created in their availability set and are hosting the Parallels RAS SCG as mentioned in Steps 1 and 2, you can move on with creating the actual Azure Load Balancer.
Load balancing provides a higher level of availability and scale by spreading incoming requests across multiple VMs.
We will create a public basic load balancer from the Azure portal.
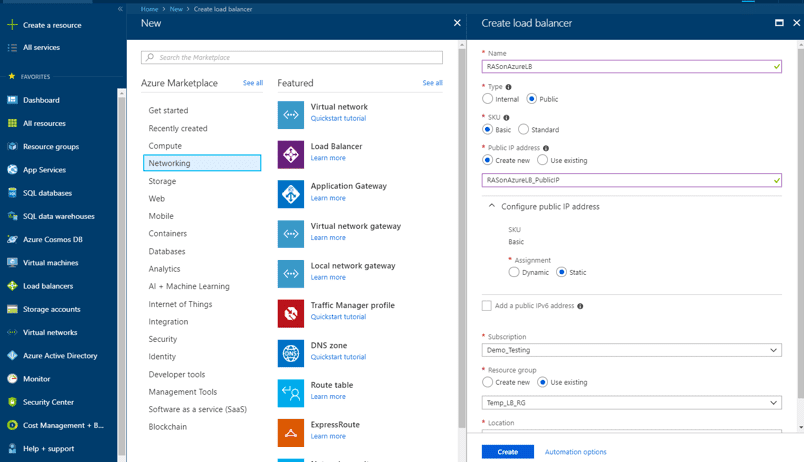
- On the upper-left side of the portal, select Create a resource> Networking > Load Balancer.
- In the Create load balancer pane, enter these values:
Name of the load balancer: RASonAzureLB
Typeof load balancer: Public
Create a new public IP or use an existing one. In this example, we created a new public IP, RASonAzureLB_PublicIP, with SKU set as Basicand Assignment set as Static.
Make sure that the correct subscription is chosen.
Create a new resource group or use an existing one. In this example, a new resource group has been created. - Select Create.
Note: This deployment is based on a Basic SKU; however, both Basic and Standard can be used. Learn the difference between a Basic and Standard SKU.
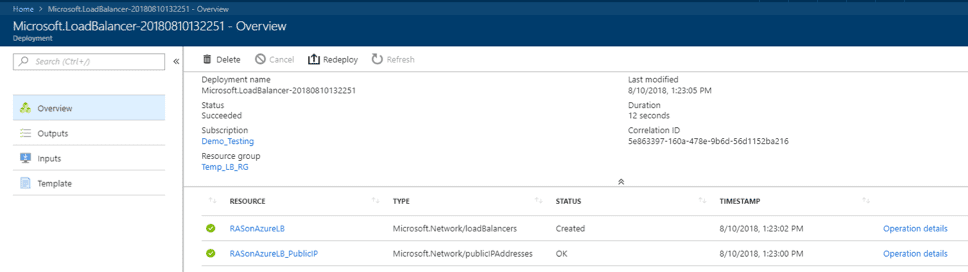
Once deployment is successful, you should see the resources created, including the Azure Load Balancer and the public IP.
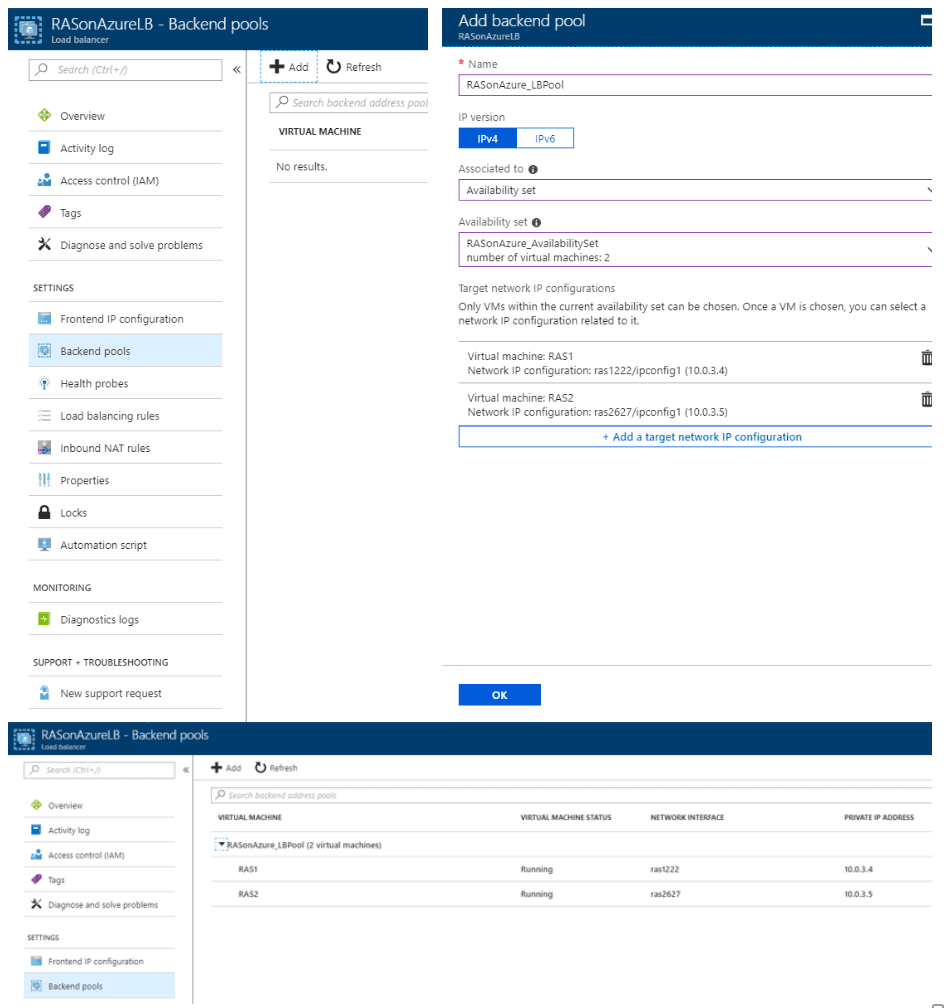
Step 4 – Create a Back-End Pool
To distribute traffic to the VMs created earlier, a back-end address pool needs to be created. This will contain the IP addresses of the virtual NICs that are connected to the load balancer.
Create the back-end address pool RASonAzure_LBPool to include RAS1 and RAS2 acting as RAS SCGs from the availability set created in Step 1.
- Select All resourceson the left menu, and then select RASonAzureLB from the resource list.
- Under Settings, select Backend pools, and then select Add.
- On the Add a backend poolpage, do the following, and then select OK:
- Name: RASonAzure_LBPool.
- Associated to: From the dropdown menu, select Availability set.
- Select the Availability set.
- Select Add a target network IP configuration to add each virtual machine (RAS1 and RAS2) that you created to the back-end pool.
We need to create a rule to choose what traffic is going to be load balanced onto our load balancing pool. Prior to this, at least one health probe must exist.
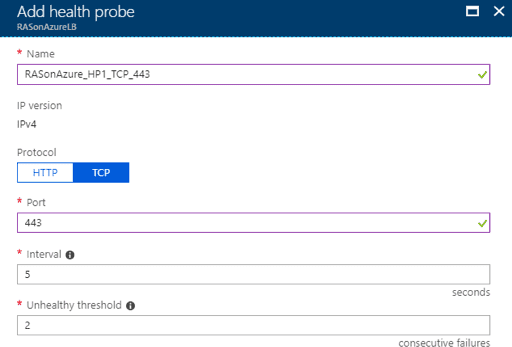
Step 5 – Create a Health Probe
The load balancer created previously needs to monitor the status of the back-end servers to be able to distribute traffic successfully. This can be achieved by using health probes. The health probe dynamically adds or removes VMs from the load balancer rotation based on their response to health checks.
Using the Azure Portal, we can create a health probe.
- Navigate to Load balancer settings > Health probes.
- Click +Add.
- Configure the below settings for your health probe:
-
- Name: RASon Azure_HP1_TCP_443
- Protocol: In this case, we choose TCP.
- Port: In this case, we choose 443. (This is the default secure port that the Parallels SCG is listening on. If this is changed from the Parallels RAS Console, this health probe should reflect this change.)
- Interval: Signifying the amount of time between probe attempts. By default, the minimum value is five seconds but can be changed as required.
- Unhealthy threshold: Specifies the number of consecutive probe failures that must occur before that particular VM is considered unhealthy/down. By default, the minimum value is two consecutive failures but can be changed as required.
It is recommended to create a health probe for each load balancing rule specifying the port and protocol.
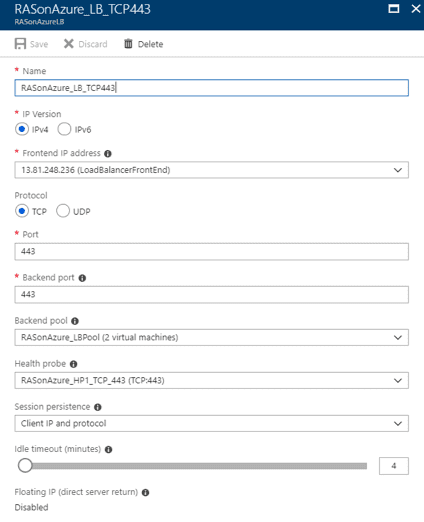
Step 6 – Creating Load Balancing Rules
A load balancer rule is used to define how traffic is distributed to the VMs—in our case, the Parallels SCGs. We will configure the front-end IP configuration for the incoming traffic and the back-end IP pool to receive the traffic, along with the source and destination ports.
Create a load balancer rule named RASonAzure_LB_TCP443 for listening to port 443 in the front-end load balancer. The rule is also for sending load-balanced network traffic to the back-end address pool RASonAzure_LBPool, also by using the health probe RASonAzure_HP1_TCP443.
- Select All resourceson the left menu, and then select RASonAzureLB from the resource list.
- Under Settings, select Load balancing rules, and then select Add.
- Use these values, and then select OK:
- Name: RASonAZure_LB_TCP443
- Protocol type: TCP
- Port number: 443
- Back-end port: 443
- Name of back-end pool: RASonAzure_LBPool
- Name of health probe: RASonAzure_HP1_TCP443
- Session persistency: Client IP and Protocol
- Note:
- Optional: Add another TCP 80 load balancing rule if you require auto-redirection from 80 to 443.
- When using Azure Load Balancer, UDP traffic is not load balanced.
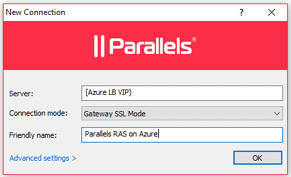
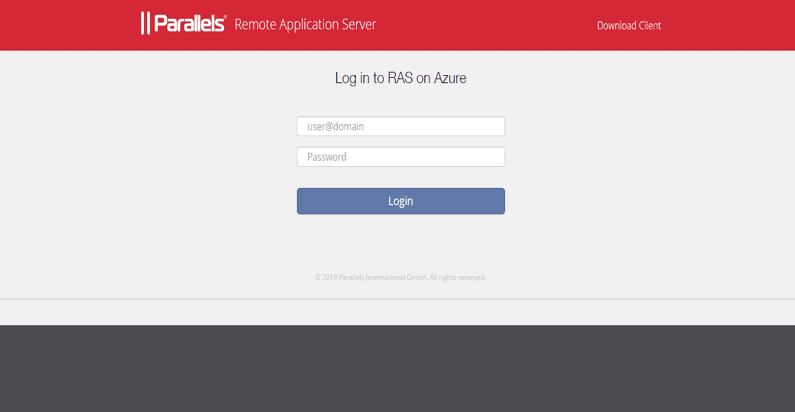
Step 7 – Evaluate
The final step is to test the Azure Load Balancer that was deployed to load balance front-end traffic to the Parallels Secure Client Gateways.
Testing can be done from the native Parallels Client installed on the device or from the HTML5 Client portal. Put in the Azure Load Balancer Virtual IP (VIP) or DNS name that should load balance traffic to one of the specified Secure Client Gateways.