What Is RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)?
Remote desktop protocol (RDP) is a proprietary communication protocol developed by Microsoft that lets users connect to another PC from a remote location. It securely allows remotely connected computers to share information over an encrypted communication channel. But what is RDP in great detail, and why is it the most used remote access protocol?
This post delves deeper into explaining what RDP is, its features, use cases, and drawbacks. You’ll also learn more about enabling RDP in Windows 10 and 11 and how Parallels RAS can enhance Microsoft remote desktop services (RDS).
RDP Features
RDP is a secure, interoperable protocol that you can leverage to create safe connections between clients, servers, and virtual machines (VMs). It extends the T.120 point-to-multipoint communication protocols standardized by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) as the underlying solutions for teleconferencing, videoconferencing, and computer-supported collaboration.
It’s an exclusive protocol developed by Microsoft that furnishes users on one desktop with graphical user interfaces (GUIs) they can use to connect to other machines over a network. For this to work, users need to install an RDP client on their endpoints from which they can leverage to access other computers running the RDP server.
There are numerous RDP clients for most operating systems (OSs), including Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, Unix, and Android. On the other hand, RDP servers are built exclusively into Windows OSs. By default, the RDP server listens for RDP connections on port 3389.
When using the protocol, the RDP port opens an encrypted network channel between the local and the remote computers. This allows signals, such as keystrokes, mouse movements, and desktop displays, to be transmitted back and forth securely between the client and the server.
Some notable features that RDP support include:
- Smart card authentication. RDP allows users to sign into RDP servers with a smart card by entering a PIN on the client application and sending it to the RDP session host server.
- Bandwidth reduction. RDP can dynamically adjust various parameters, such as network bandwidth availability and computing resources, to deliver the best possible user experience.
- Multiple displays. The protocol allows users to operate a computer with multiple monitors.RemoteFX virtualized graphical processor unit (GPU). RemoteFX is an RDP feature that enables Hyper-V VMs to share a physical GPU for high-burst workloads.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS). RDP supports TLS protocol that enables the client to verify the authenticity of the remote desktop session host (RDSH) server by encrypting all the connections between them.
- Clipboard sharing between local and remote computers. Users can easily copy/paste files from their local computers to remote desktop sessions with RDP.
- Use of local devices in remote desktop sessions. The protocol allows users to leverage local devices in remote desktop sessions, including printers, hard drives, shared drives, and USBs.
What is RDP? – Use Cases
There are four primary use cases of RDP:
- Remote desktop administration. IT teams can leverage the protocol to provide technical support to remote employees. They can view and take over an employee’s remote desktop session, allowing them to diagnose and fix issues from a remote site.
- Remote access. RDP facilitates anywhere, anytime access to corporate resources. For example, employees on vacation or those traveling can access their workplace computers and work from any location.
- Conducting demos. Users can leverage RDP for the demonstration of applications or processes that are usually accessed only from their offices. For example, an employee could prepare the demo on their workplace computers and display it on another endpoint elsewhere, such as the client’s office o conference room.
- Access to powerful computational resources. RDP can enable users to leverage low-computational devices, such as terminals, to access a powerful workstation in the office.
How to Enable RDP on Windows 10 and 11
You can leverage RDP on your endpoint to connect to Windows 10 or 11. Let’s walk through the steps required to activate RDP on Windows 10 and 11.
Windows 10
By default, the RDP feature is disabled on Windows 10 Pro; therefore, you need to enable it. There are various ways you can enable the RDP feature. First, let’s review the most straightforward approach:
- Click the Start button and type “Settings.”
- Next, click “System”> ”Remote Desktop.”
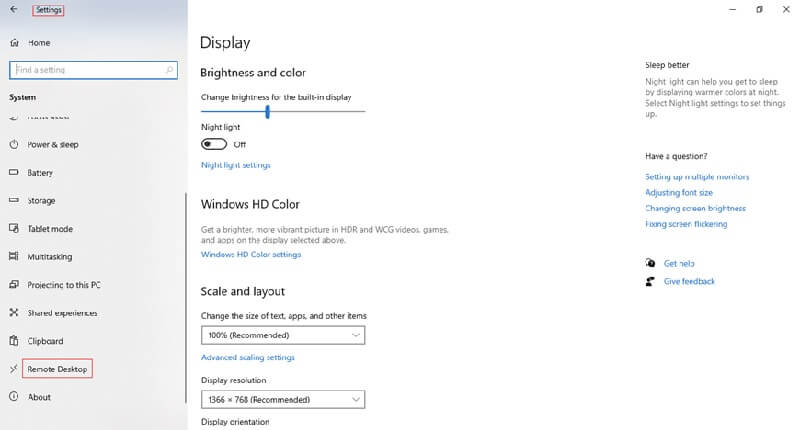
- Click on the “Enable Remote Desktop” toggle button. Click the “Confirm” button to complete the process.
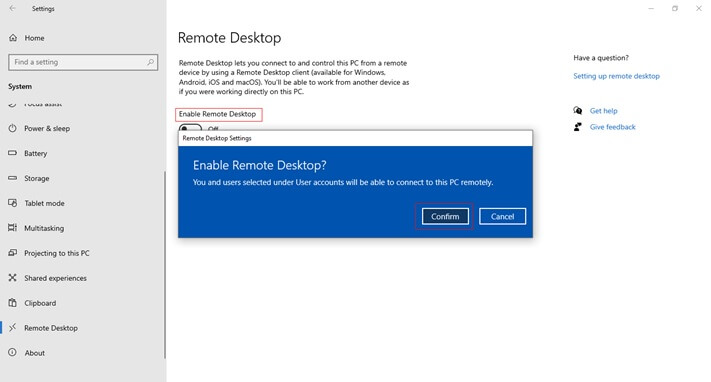
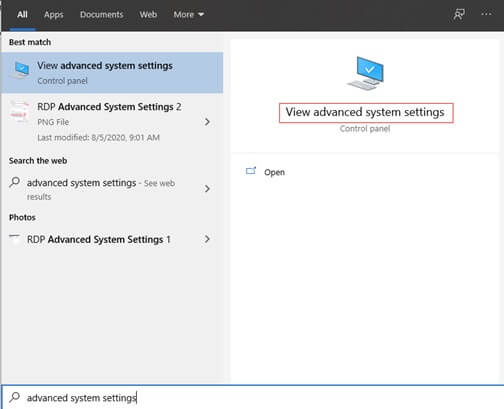
You can also enable the RDP feature through System Properties as follows:
- Click the Start button, type “Advanced System Settings.”
- Click on the “View Advanced System Settings.”
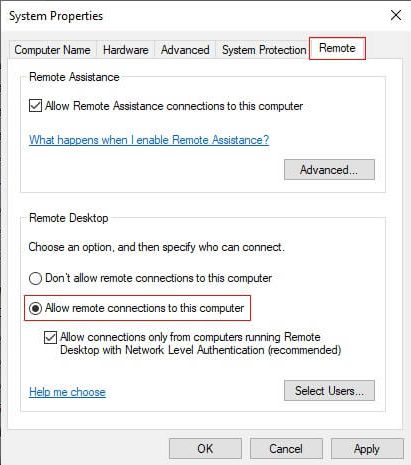
- Click on the “Remote” tab
- Enable the “Allow remote connections to this computer” checkbox.
Windows 11
Follow these steps to set up the RDP server or the computer you want to connect to:
- (Ensure you have Windows 11 Pro. To verify whether you have Windows 11 Pro or not, click the “Start” followed by “Settings.” Under “System” settings, select “About,” and under “Windows specifications,” look for “Edition.”
- If the edition of the OS is Windows 11 Pro, click the “Start” followed by “settings.” Then under “System,” click “Remote Desktop.” Set the “Remote Desktop” feature to On and confirm the settings.
- Note the name of your RDP server under the PC name, as you’ll need this later when connecting to the computer.
Follow these steps below to establish a connection to the RDP server that you’ve set up:
- Type “Remote Desktop Connection” in the search box of your local Windows PC, then click “Remote Desktop Connection.” Type the name of the RDP server you want to connect to (from step 1) and select “Connect.”
- For Android or iOS devices, download and install the appropriate RDP client from Google Play or App Store. Next, open the application and add the name of the RDP server you want to connect to (from step 1). To connect to the server, simply choose the PC name you added and wait for the connection to be completed.
What is RDP? – The Drawbacks
While RDP has notable benefits, including remote access and simplifying IT administration, the protocol has some limitations. Let’s examine some of these drawbacks.
Common connectivity issues with RDP
As useful as the RDP feature is, things can go wrong when trying to establish a remote connection to the server. Common connectivity problems include:
- Network failure
If there’s no valid communication path between the client and the server, you’ll not establish a remote connection. This usually happens because some network resources such as routers aren’t working as they are supposed to. It’s appropriate to test the connectivity between the client and the server. - Disabled RDP feature
By default, the RDP feature is disabled. When you establish a connection to a disabled RDP server, the connection fails. - Firewall issues
A typical scenario you’re likely to come across is that of blocked ports or conflicts with port assignments. For a reliable remote connection, you need to ensure that the default RDP port (in this case, 3389) is not blocked on the server. Also, you have to ensure that the port is assigned to RDP. - DNS issues
If the server’s IP address changes, clients cannot establish a remote connection. Unless you manually clear the cache and force a fresh DNS resolve mechanism, a remote desktop connection is impractical. In some cases, clients cannot connect to the server if they are using an external DNS server that can’t resolve hosts on the company’s private network. - Authentication issues
If the client lacks the necessary permissions to login onto the RDP server, Windows displays an authentication error message. You need to add the account to the “Remote Desktop Users group” or “Administrators group” to authenticate such a user to the RDP server. - Exceeded connections
Sometimes the RDP server can surpass the maximum allowed connections. Some servers may also refuse client connections if they are too busy or if the remote desktop connection is likely to weaken their performances. - Dropped connections
If the available bandwidth is incapable of supporting RDP requirements, you’ll experience dropped connections. Under such circumstances, you need to close any bandwidth-intensive applications.
Security Issues
| Date reported | Vulnerability | Description |
|---|---|---|
| July 2019 | Reverse RDP attack (CVE-2019-0887) | It allows an authenticated attacker to abuse the RDP’s clipboard redirection and runs code on the remote server. It can affect unprotected remote connections on Windows 7, 8, and 10. It can also affect Windows Server 2008, 2012, and 2016. |
| May 2019 | BlueKeep attack(CVE-2019-0708) | BlueKeep is a wormable malware. As such, it can replicate to all the nodes within a network without any permission from users. It can affect unprotected remote connections on Windows XP, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008. |
| May 2019 | Skype for Android Information Disclosure (CVE-2019-0932) | It allows the malefactor to access the Android-based Skype app by listening and recording voice calls. For business executives who use Skype regularly, CVE is a potential RDP vulnerability problem. |
| December 2018 | WER attack (CVE-2019-0863) | It exploits the Windows Error Reporting (WER) protocol to execute code on the unrestricted system linked via RDP. It allows the malefactor to download, delete, and create new administrator accounts. It can affect unprotected remote connections on Windows 7, 8, and 10. It can also affect Windows Server 2008, 2012, and 2016. |
Microsoft RDP Limitations
Since the release of Windows Server 2008 R2 OS, Microsoft has referred to Microsoft RDP software as Remote Desktop Services (RDS). However, RDS-based application and desktop delivery as a standalone solution can create some hiccoughs in an organization’s activities.
There are a number of concerns that commonly arise when using Microsoft RDS alone:
- Tedious setup and maintenance
- Limited experience on mobile devices
- Lacks automatic load-balancing
- Printer redirection
How Parallels RAS Enhances Microsoft RDS
From installation to effectively managing the remote infrastructure, IT administrators face a tough challenge with Microsoft RDS. Most features do not come auto-configured, and it requires expertise and experience to successfully deploy and operate them.
Parallels RAS is easy to deploy and straightforward to manage, allowing seamless and fast delivery of applications and desktops. Parallels RAS includes load balancing features and reinforces data security with multifactor authentication, advanced granular filtering and client policies.
Excellent Client User Experience, Even on Mobile
In contrast to Microsoft RDS, Parallels RAS enables you to deliver Windows applications to any device and platform, including Mac, Linux, iOS, Android, HTML5, and Chrome OS. This allows IT staff the flexibility they need to deploy a full bring-your-own-device (BYOD) or carry-your-own-device (CYOD) policy.
Want to take try out Parallels RAS? Download a 30-day trial.

