Network Troubleshooting your Parallels Desktop VM
Network troubleshooting commands are important for any VM user.
Today we can’t imagine our life without information technology. Access to all this data wouldn’t be possible the actual network connection. Almost all the modern devices nowadays have a way to connect to the the network. Your Mac and Parallels Desktop virtual machine are no exception!
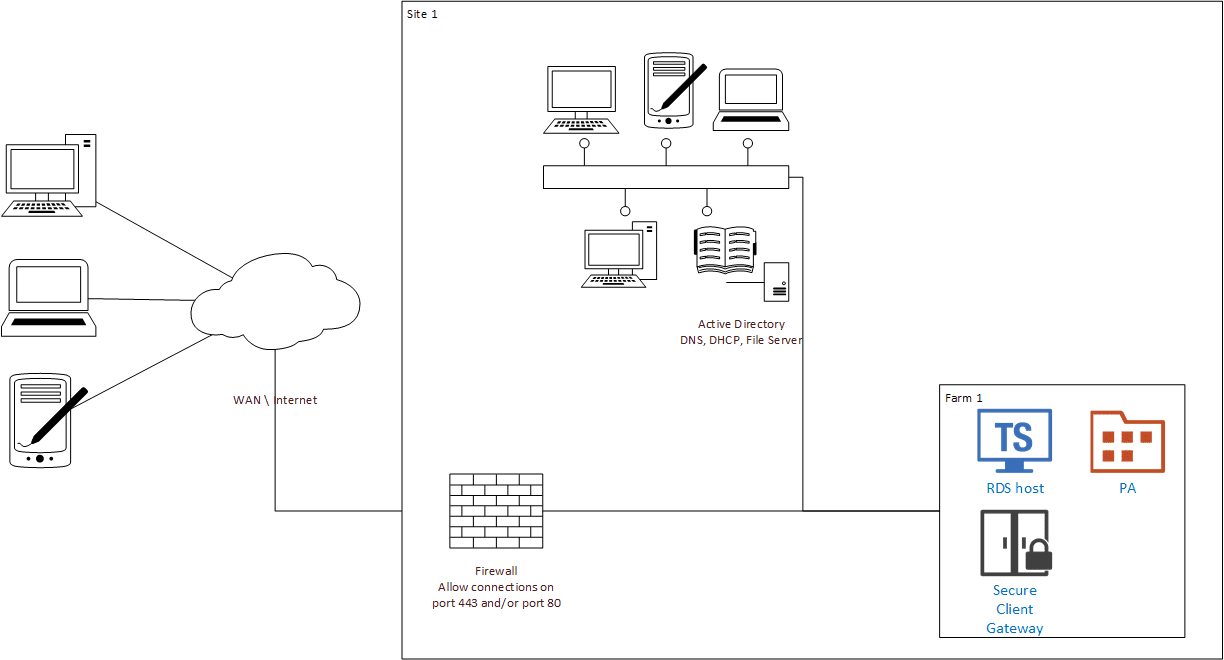
There are several network modes in Parallels Desktop which we covered is one of the past blogs: Bridged, Shared and Host Only network. Let’s summarize the purpose of each in brief:
With Shared mode, we use the Mac connection to connect to the external network. It’s the easiest to use because your VM can use any type of network connection available on the Mac to connect to Internet (Ethernet, wifi). Bridged mode is used when you want your VM to establish direct connection with your Mac network card. In Bridged mode your VM will look like a standalone PC on the network. And last but not least is Host only mode. Host-Only network is a closed network that is accessible only to Mac OS X and Windows. Select this option to allow the VM to connect to the host computer and the VMs residing on it and to make it invisible outside of the host computer.
But what if something went wrong? What if the default virtual machine setup does not let you surf the internet from Parallels Desktop side, what if the app hangs out which force quit command to use? Don’t panic. We’ve got some easy troubleshooting steps. By the way – many of the steps below are applicable to Windows PCs (not only virtual machines).
First you need to check the network connection on the Mac side. Mac shares the network connection with the VM, and if you can’t connect to any website from the Mac side you won’t be able to do it from your VM. So in this case you need to check all of Mac settings and contact your provider or system administrator for help.
Once you’ve checked the network connection on the Mac side you should do the same thing on the virtual machine side. But in virtual machine we need to perform a bit more steps and actions, because the reason for the dropped network connection could be different.
As a first step, check the Parallels Tools performance. A specific component of Parallels Tools works as a sharing of network between Mac and VM and if it has not been installed correctly, that may be the network issue. We can simply reinstall it with the following steps:
- Launch Windows virtual machine.
- Disable antivirus in Windows.
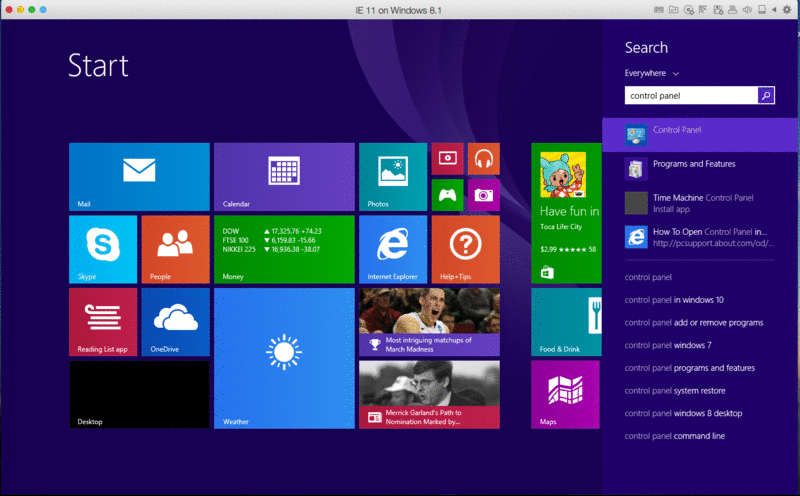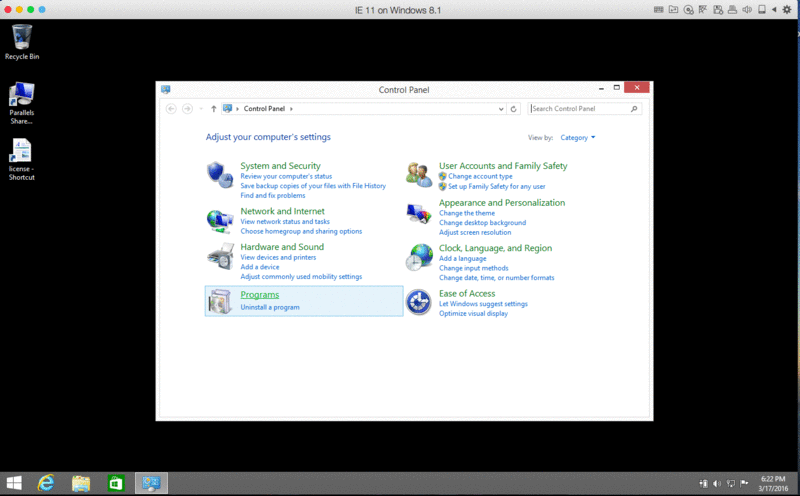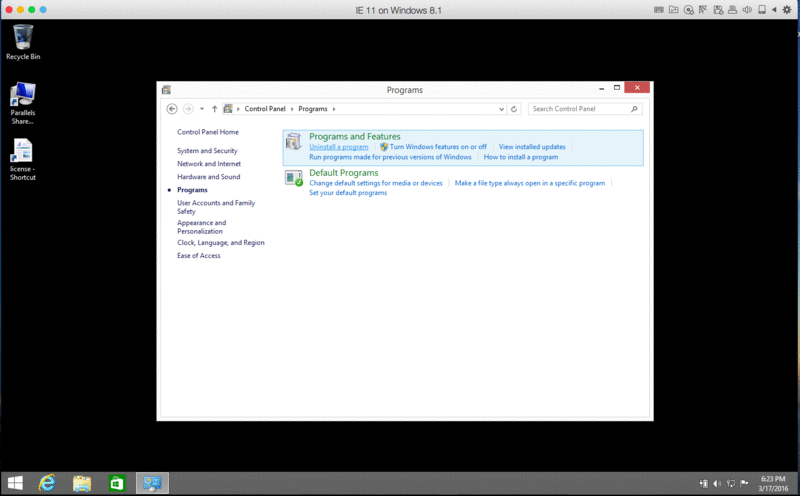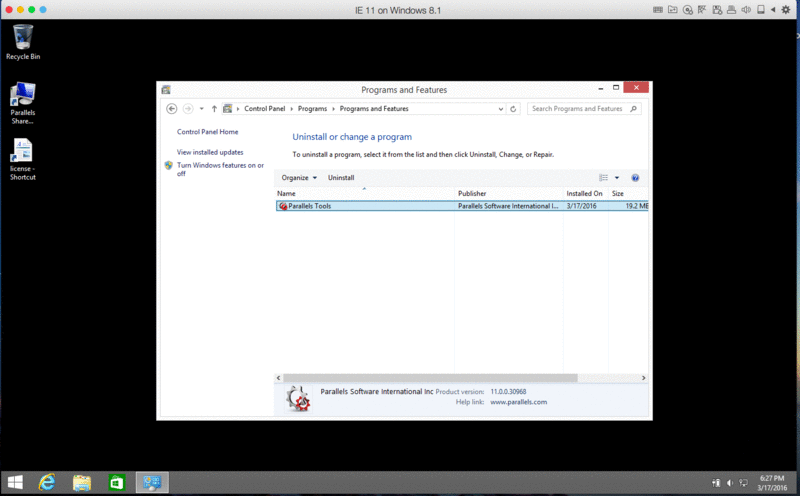
- Open Control Panel > Programs and Features (Uninstall a program for Windows 10, or Add/Remove programs for Windows XP) and remove Parallels Tools if present.
- Restart Windows.
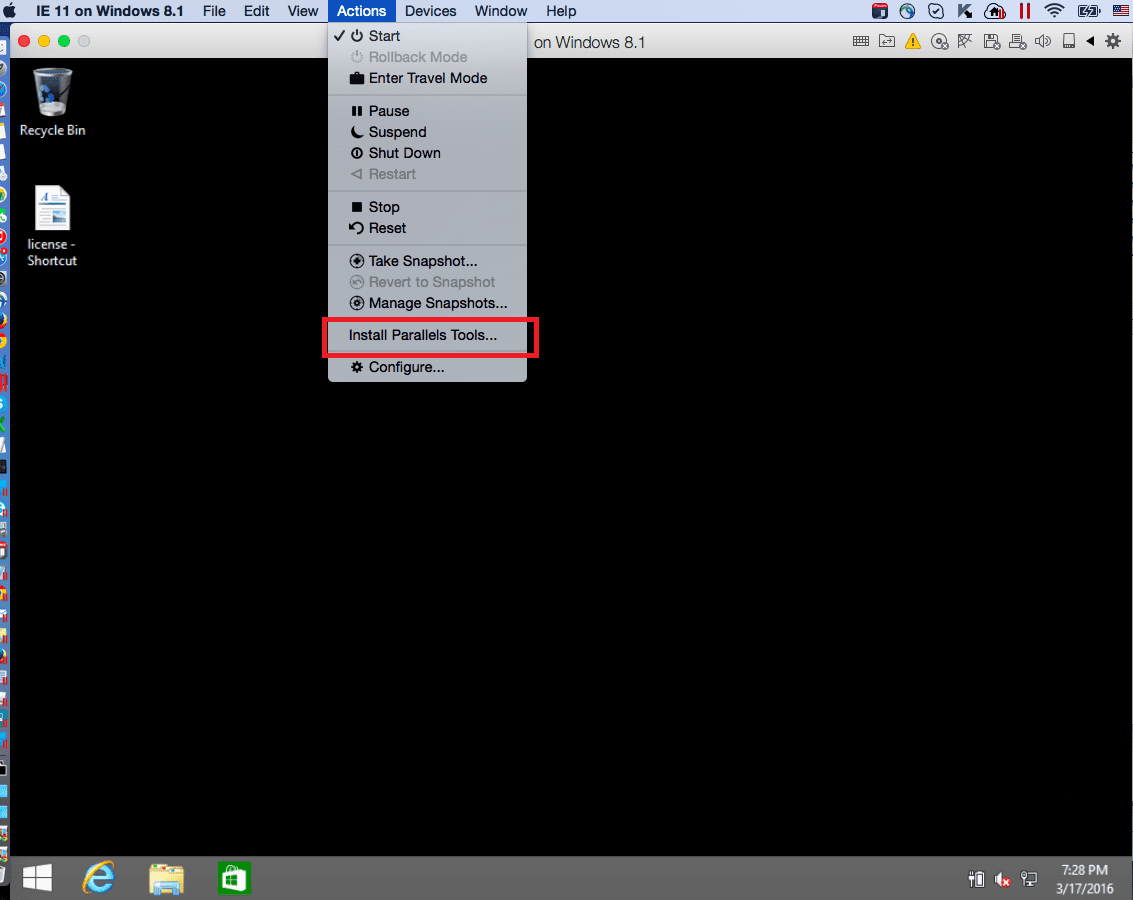
- In Mac menu bar click on Actions (Virtual Machine in older versions) > Install Parallels Tools.
- Restart Windows again.
- Enable your antivirus back.
Once the Parallels Tools have been reinstalled we can check performance of this component to make sure that everything has been installed and works correctly. To do that we need to use the following steps:
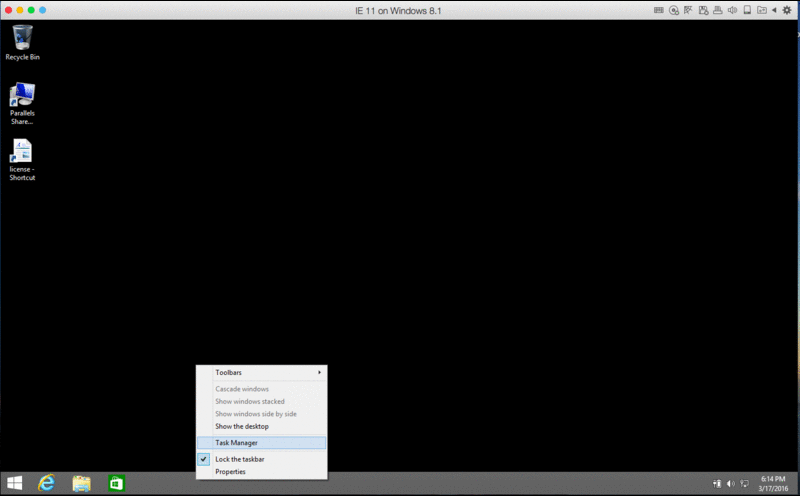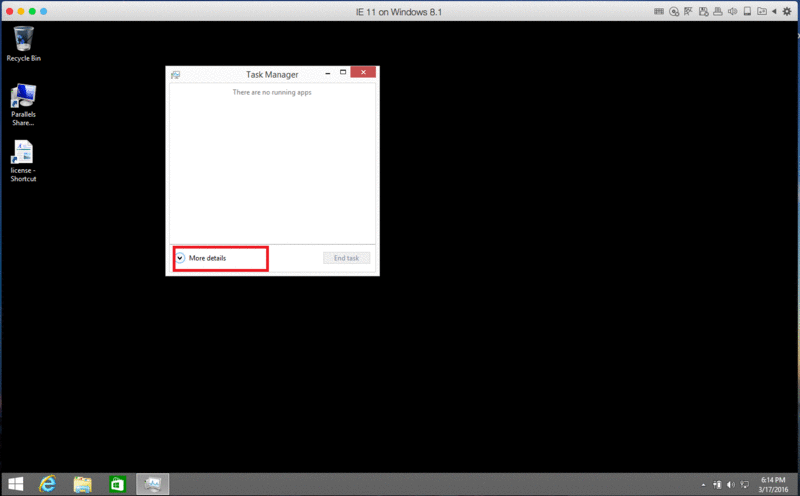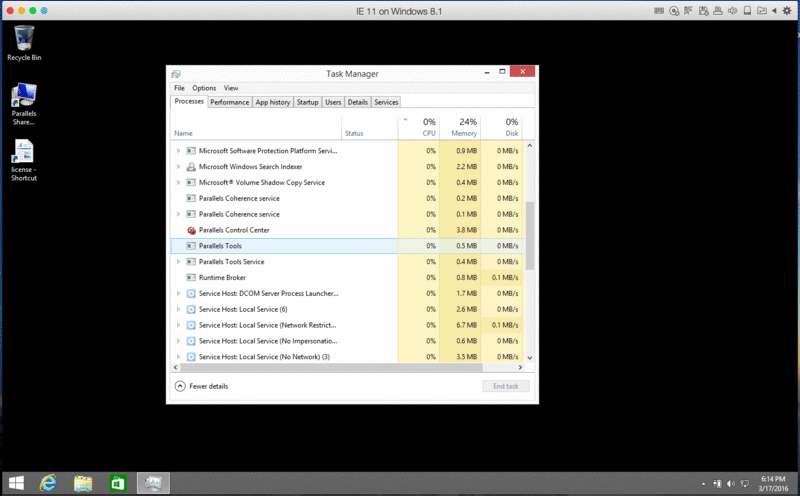
- Open the Task Manager and find the following processes in process tab: (In Windows 8 you need to click “More details” button > then you will be able to find out the “Process” tab)
- Go through processes and make the Parallels Tools and Parallels Tools Service processes are running.
Check the connection now. Everything works fine now? Perfect! Still an issue? Read on.
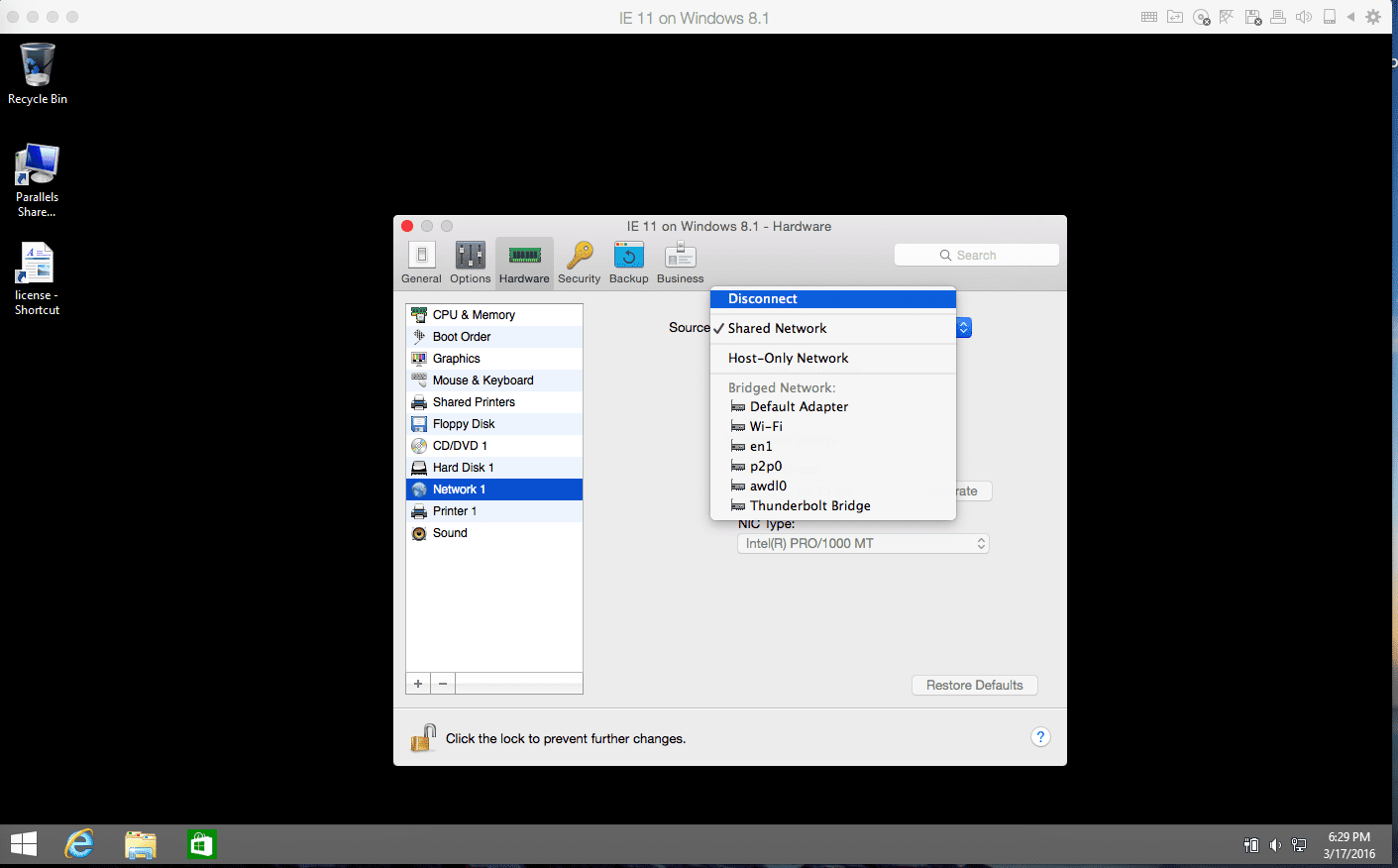
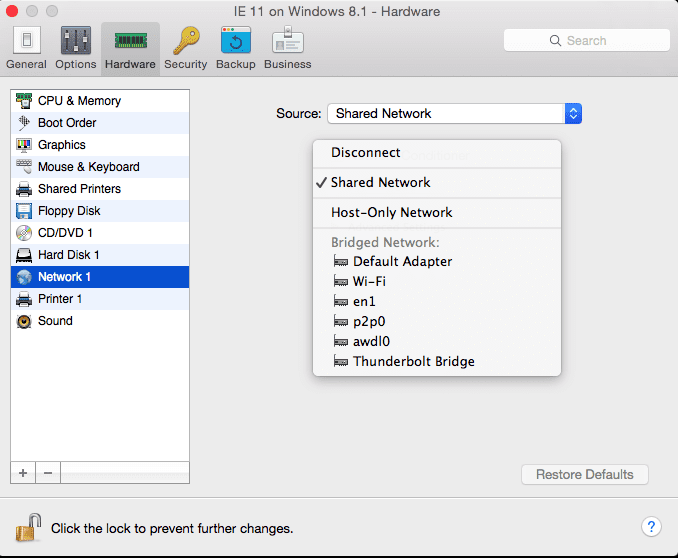
As a next step you need to check and adjust the virtual machine configuration; Check the network adapter status (and if it’s there at all).
- Go to Configuration > Hardware > Network 1 and verify that one of the network modes has been used. If you find the “Disconnect” status change it to the “Shared mode”.
Virtual machines use the Shared mode by default, but sometimes it may be set to Bridged or the Host only. In this case we need to switch between modes back and forth, for example between Bridged and Shared.
This simple steps will help your VM to configure some internal important settings and set it up correctly.
After that we need to check one more configuration setting – OS type. Go to the General tab, and verify that the operating system matches the OS currently installed in your virtual machine. Sometimes it may have changed after you upgraded the operating system inside your virtual machine.
Now that you’ve checked your VM configuration and if the network connection still doesn’t appear, we need to continue our troubleshooting on the Windows side.
Let’s revert back to the Network adapter, but at that time we will check it in Windows Device Manager. To open the Device Manager, follow these steps:
- For Windows XP: Click Start > Control Panel > Performance and Maintenance > System. Then go to the Hardware tab and click Device Manager.
- For Windows Vista/7: Click the Start button, then scroll to the Control Panel > System and Maintenance then select Device Manager.
- Windows 8: Click the Start button, type ‘Control Panel’ without quotes > System and Maintenance then select Device Manager
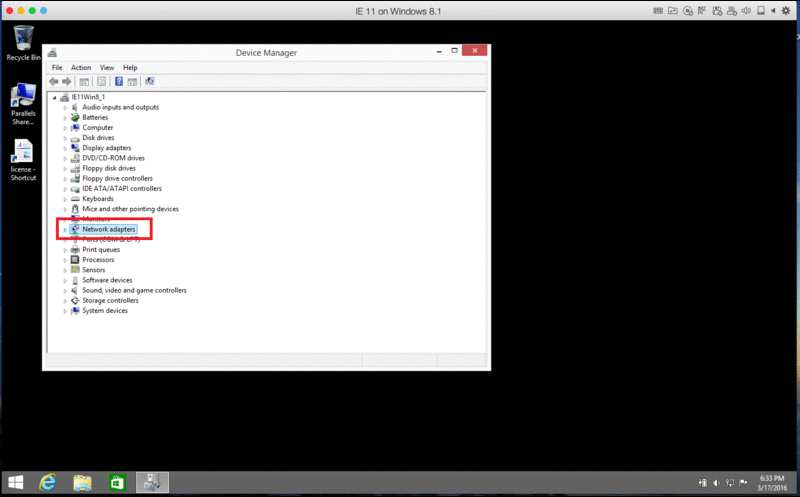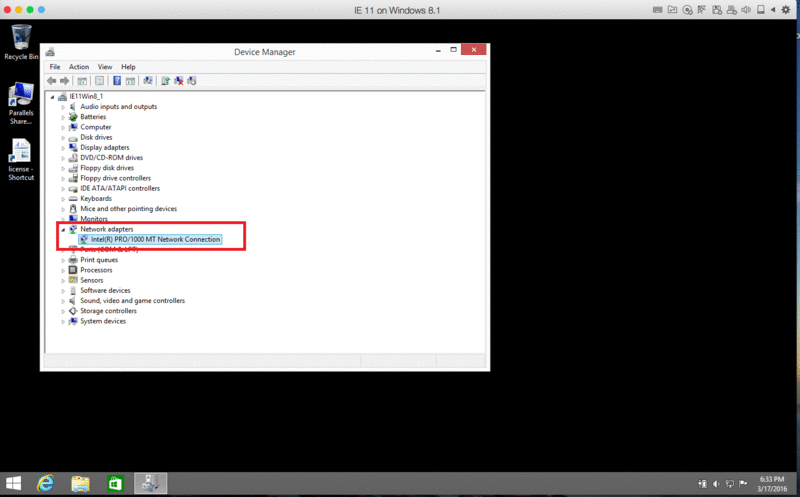
Check the network adapter’s name. It should be either a Parallels Network Adapter or Intel PRO/1000 MT Network Connection. If you see any other name (e.g., Ethernet Controller) right-click it and select Uninstall. Then Right-click on Computer in the Device Manager and choose Scan for hardware changes.
Restart Windows and check if the Internet connection is working now. After these steps we need to check a few other adapter settings. For example, if you are using an AirPort router (capsule) in Bridged mode or any network in Shared mode, make sure that Properties are set to Internet Protocol v4, Obtain IP and DNS automatically is selected instead of manual configuration.
Alright, still no connection? There is one more method to find the reason and fix the issue with network connection. First, let me explain to you some troubleshooting steps in Command Prompt.
Command Prompt is known as cmd.exe or cmd (after its executable file name), is the command-line interpreter on Windows NT, Windows CE, OS/2 and eComStation operating systems, and it interacts with the user through a command-line interface. In Windows, this interface is implemented through Win32 console. Command Prompt may take advantage of features available to native programs of its own platform.
In our case we can simply execute some commands in CMD for checking network connection and fixing issue with it. First, let’s open Command prompt and check the IPs and default gateway
- Open Command Prompt:
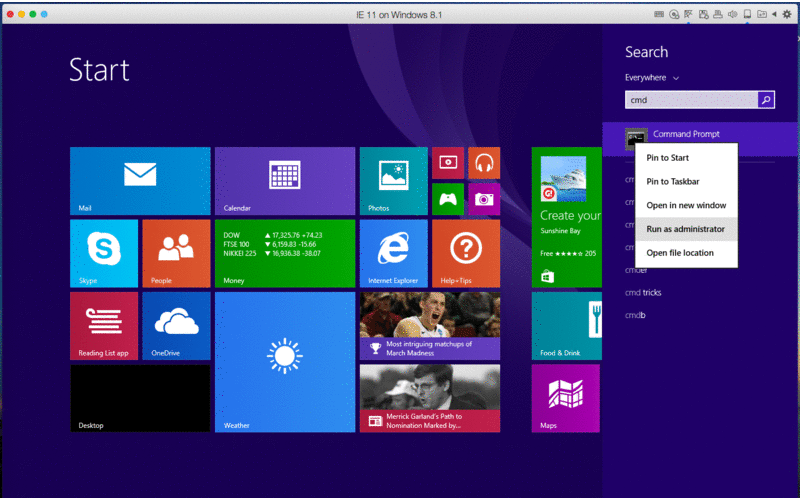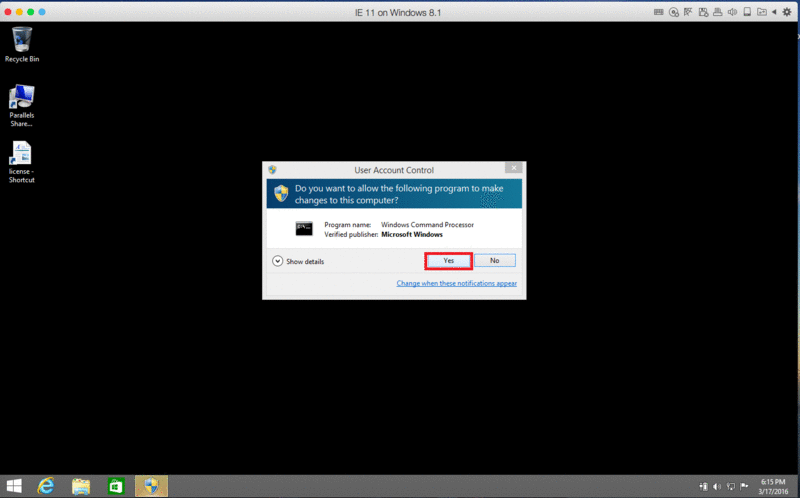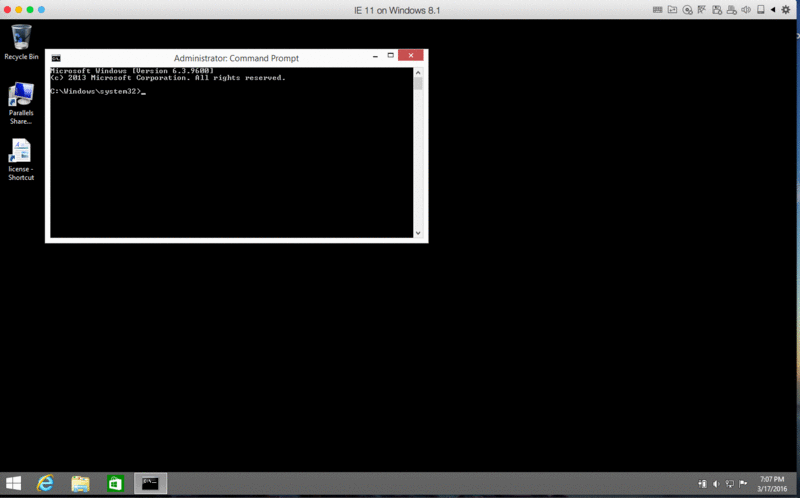
- For Windows XP: Select the Start button, then click Run… When the pop-up window appears, type CMD and hit Return/Enter.
- For Windows Vista/7/8/10: Click the Start button, then type CMD in the Search box. Right-click on CMD in search results, then click the “Run as Administrator” option. This will open Command Prompt with admin privileges.
Now we have the Black window and can type in it the following command in order to check the network configuration.
Type in:
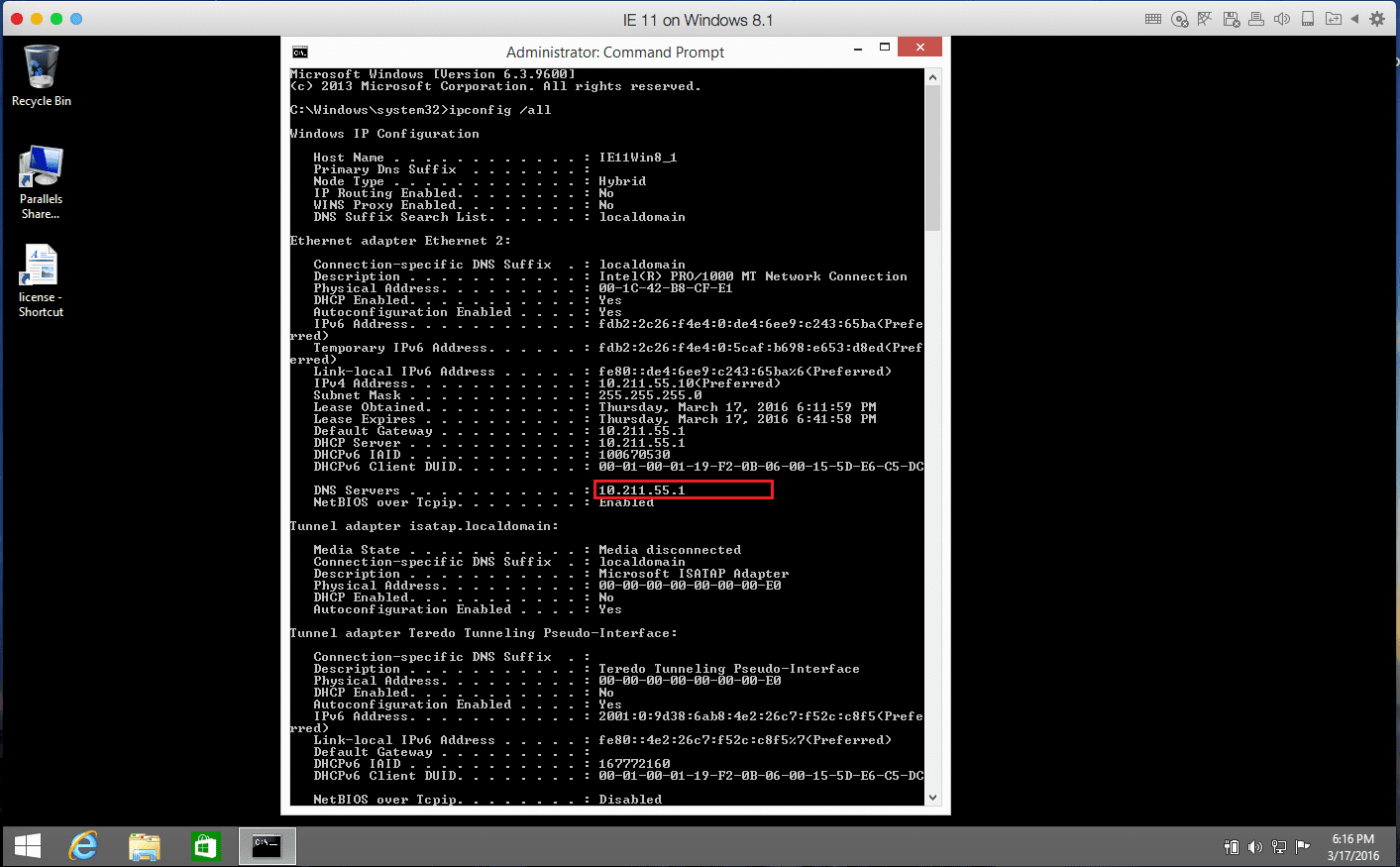
ipconfig /all
and hit Enter and check the output.
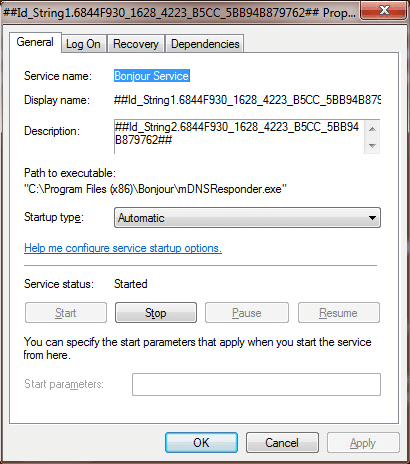
If your virtual machine is in Shared networking mode, the IP address should resemble 10.211.55.x. If you are in Bridged networking mode, the IP address should look similar to your Mac IP address, e.g. 192.168.0.10. If it is 0.0.0.0, it means that the issue related to the known incompatibility issue between Windows operating systems (it may affect all OSes) and Apple’s Bonjour service. The Default Gateway may have been set to 0.0.0.0 on a Windows Vista-based or later OS running Apple’s Bonjour service (Apple’s Bonjour service might appear on your virtual machine after installing Adobe CS3 or similar software).
In this case we can fix the issue using the following steps:
- Go to Start > Run
- Type Services.msc and hit Enter
- Find a service with a strange name, for example:
- Stop the service and change its Startup type to Disabled.
- Reboot your virtual machine.
If the “ipconfig” output is OK, we can continue our troubleshooting with other command – “ping”
We can try to ping any Parallels server for example, by entering the following command:
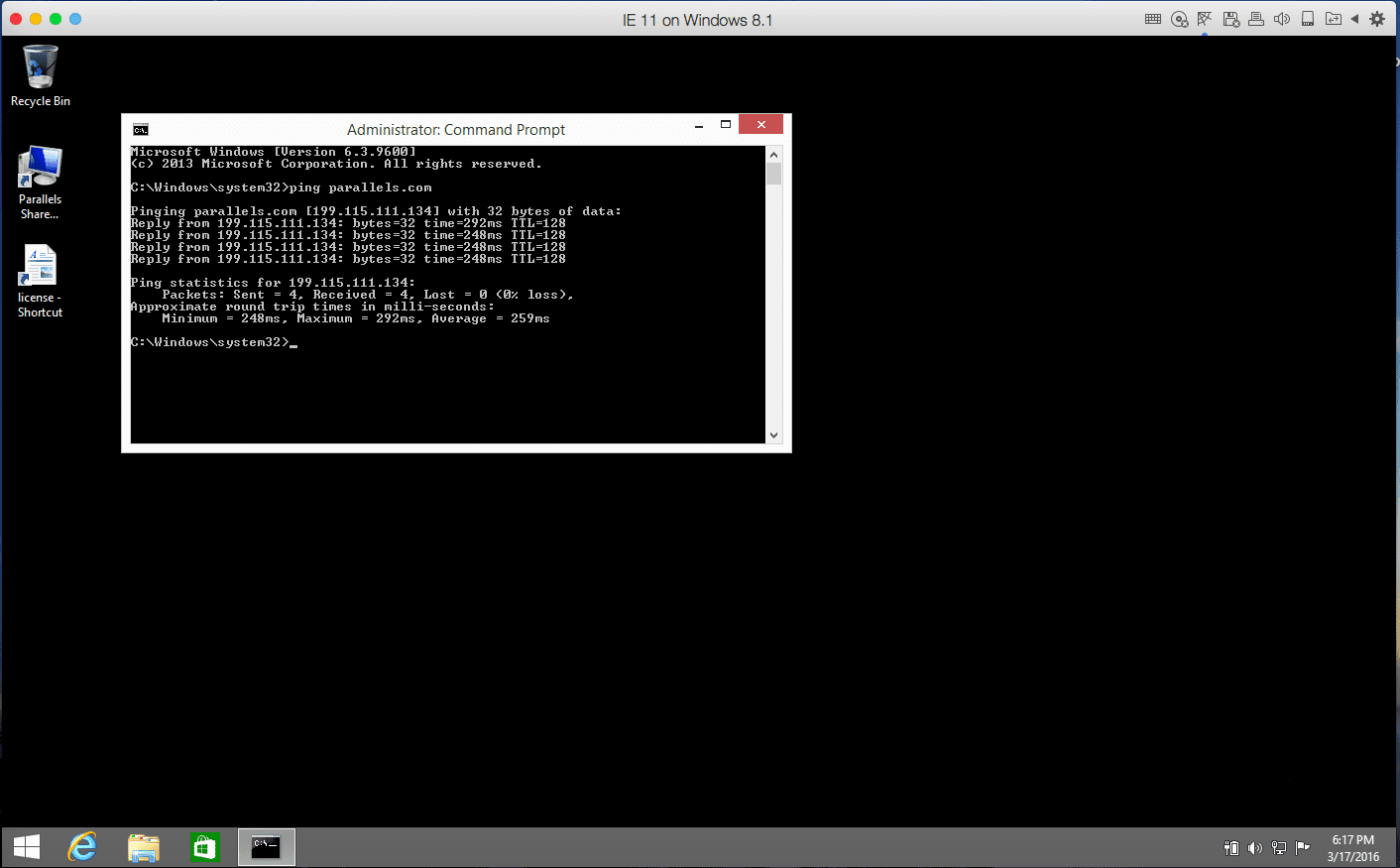
ping parallels.com
A normal reply looks like this:
Reply from 64.131.89.6: bytes=32 time=188ms TTL=54
Reply from 64.131.89.6: bytes=32 time=187ms TTL=54
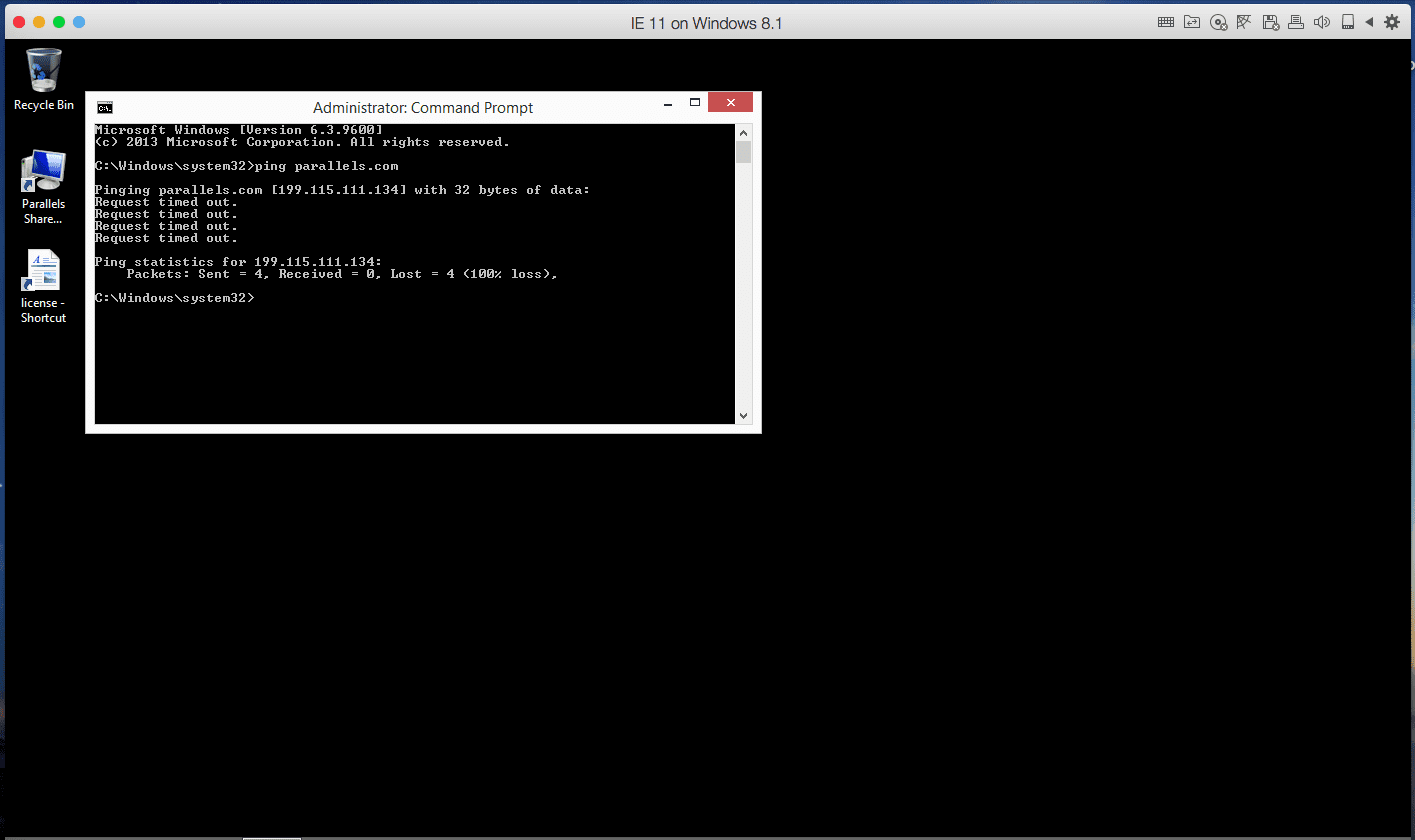
If you get this reply:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Try pinging via IP address:
ping 64.131.89.6
If you get a normal reply this time, it means that your virtual machine is in Bridged networking mode and failing to get correct DNS settings from the gateway or that you set them incorrectly. Please direct this problem to your network provider if you can’t resolve it.
Because the DNS settings and the gateway issue too is not related to the Parallels Desktop settings, it’s internal Windows issue and could appear on the real PC too. But on the other hand, we have one more tip to resolve these issue without help from your network administrator.
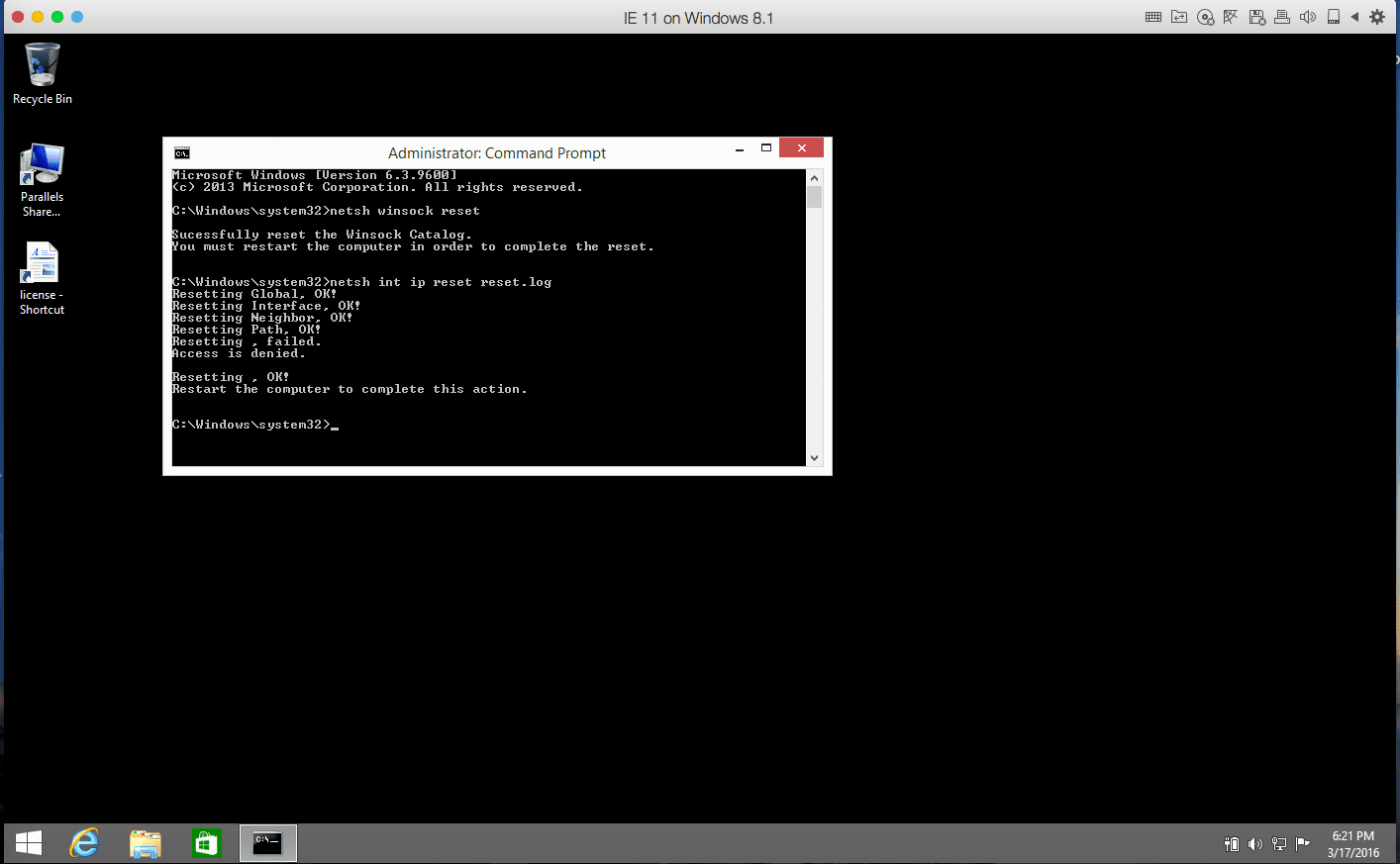
If you see “Request timed out” in both cases, try to reset the Windows TCP/IP protocol with the following commands:
netsh winsock reset
netsh int ip reset reset.log
These command will help you to reset your network adapter’s software to default and restore all default settings of Windows network adapter. You can simply type the first command, hit enter and then do the same with the second one. Now you can simply restart our Windows VM and check the network connection.
Hope you found this blog helpful and don’t forget to follow us on Twitter!
Need to run Windows on your Mac? Download our free 14-day trial.