How does a virtual machine work?
Each virtual machine is a virtualized instance of a physical machine with its own operating system and applications running in the same way as they would run on dedicated hardware.
Multiple virtual machines can run on the same physical machine, each with its own OS that functions separately from the other VMs. For example, a virtual Windows machine can run on a physical Mac computer.
Virtual machines have CPUs, memory, file storage, and customizable settings, and can run applications just like physical resources such as laptops or desktops.
What are virtual machines used for?
Virtual machines are the backbone of the virtualized computing experience. They are used for creating cross-platform development and testing environments, enabling flexible working environments and remote work, creating scalable and/or hybrid environments, and supporting disaster recovery and business continuity efforts.
More specifically, Parallels Desktop enables you to add Windows, Linux, or another operating system to your Mac by creating a VM — a virtual PC — inside your Mac.
Try Parallels Desktop risk-free and start running a VM on your Mac.
What are the benefits of using a virtual machine?
Using a virtual machine offers many benefits to organizations, including:
-
Resource optimization.
Combining multiple virtual machines on the same physical machine enables organizations to consolidate their physical IT infrastructure. -
Flexibility and scalability.
Virtual machines enable organizations to easily scale workloads and access, allowing dynamic allocation of resources based on demand. VM snapshots also enable easy replication and deployment of standardized environments, further enhancing flexibility and scalability. -
Improved compatibility and support for legacy technology.
Virtual machines run on any host system that supports the virtualization software, regardless of the host’s operating system or hardware configuration. This reduces or even eliminates compatibility issues because VMs can emulate older or outdated OSs or hardware architectures, so legacy applications can run on modern systems. -
Consistent cross platform development and testing environments.
Developers use virtual machines to create isolated, easily reproducible coding and testing environments with cross-platform flexibility. -
Disaster recovery and business continuity.
VMs can be a key part of business continuity plans because they allow organizations to operate independently of hardware and geographic restrictions. VMs help facilitate rapid recovery from disasters by enabling isolation and segmentation, offering testing environments, and allowing for automation. -
Sustainability.
Leveraging VMs allows organizations to reduce their overall hardware footprint, leading to cost savings and reduced needs for power, cooling, and physical space.
How does cloud computing use virtual machines?
Virtual machines are used by cloud providers to cover a variety of use cases where it would not be as practical or cost-effective to use physical machine. These VMs are generally hosted in data centers on servers that can act as hosts to multiple virtual machines. Some examples include running Software as a Service (SaaS) applications, browser isolation, and backing up and providing remote access to data.
How does a virtual machine support gaming and graphics?
With a virtual machine, you can play games designed for multiple operating systems on the same physical machine. The virtual machine serves as an emulator that lets you play games that are not designed for your hardware’s native operating system.
For example, you can play games designed for Windows PCs on a Mac using Parallels Desktop (enable 3D acceleration if the game requires a video card with DirectX or OpenGL support).
Types of virtual machines
There are two primary types of virtual machines, system machines and process machines.
-
System virtual machines.
These virtual machines are completely virtualized replicas of a physical machine. Multiple system virtual machines can utilize the same hardware resources, or multiple virtual machines can exist simultaneously and separately on the same physical host machine.Example use case: Any situation where a user needs to run multiple operating systems on the same physical machine, e.g., an end user wants to play a PC game on their Mac laptop.
-
Process virtual machines.
These virtual machines emulate the execution environment of a single process or application, rather than a complete operating system.Example use case: A software developer building an application that needs to work on multiple operating systems may leverage process virtual machines like Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and .NET Framework’s Common Language Runtime (CLR).
Examples of virtual machines and operating systems
-
Windows virtual machines.
A software emulation of a physical computer that runs the Microsoft Windows operating system in a virtualized environment. A virtual Windows machine enables users to install and run Windows applications just like they would on a physical machine, and behaves like a separate instance of Windows, running independently of the host operating system.Example use case: A Mac user who wants to run Windows-exclusive apps and games but doesn’t want the hassle of purchasing and maintaining a second physical computer.
-
macOS virtual machines.
Like a Windows virtual machine, a Mac VM is a software emulation that runs the macOS in a virtual environment. It behaves just like a physical Mac and allows users to run Mac apps and software independently of the host operating system. Note that Apple only allows the macOS to run on Apple hardware, but you can create multiple VMs or virtual Macs on the same Apple computer.Example use case: Developers who want to build and test apps for different versions of an OS can use virtual machines to create multiple isolated testing environments on a single physical machine.
-
Linux virtual machines.
Virtualized instances of Linux are a common VM use case, particularly for software development and testing purposes.Example use case: Linux virtual machines are widely used in server environments and for hosting websites, apps, and services. Developers can also use virtual machines to set up multiple instances of various Linux OSs on the same physical computer.
-
Android virtual machines.
Developers or anyone looking to run the Android operating system can create a virtualized instance of the Android OS that emulates an Android device for application development or testing purposes.Example use case: Developers can emulate a wide range of Android devices and configurations on a single physical machine, making it simple to test apps across different versions and screen sizes.
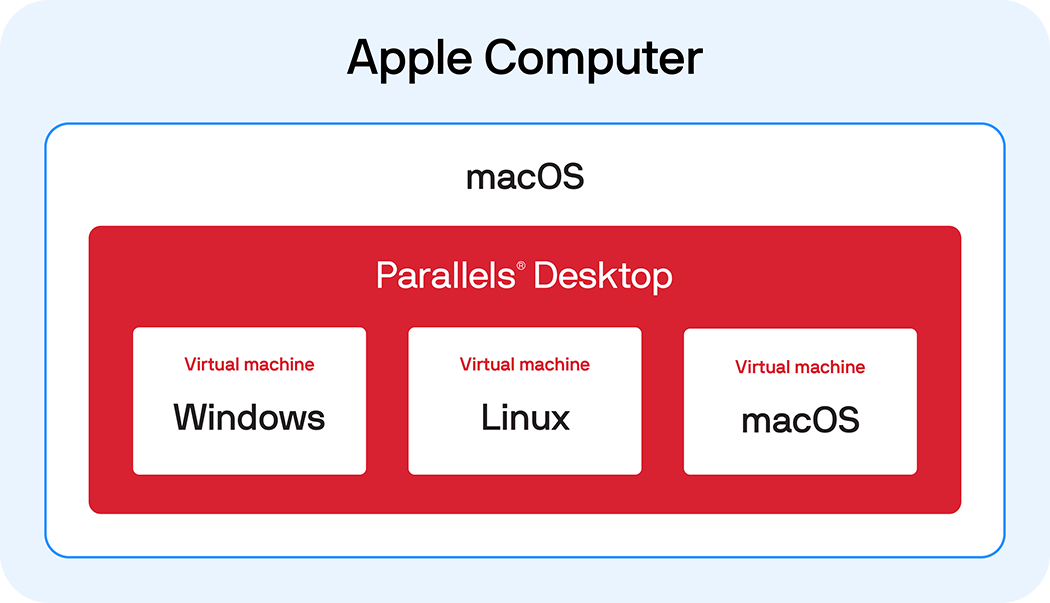
Parallels and virtual machines
Parallels Desktop is an application for Mac that enables individual users to create virtual machines and run Windows, Linux, or other operating systems and applications created for them on their Macs.
For IT administrators and their teams, Parallels Remote Application Server (RAS) is a virtual application and desktop delivery solution that centralizes applications and desktops on a server or cloud infrastructure, allowing users to access them securely anytime, from anywhere.
Resources
Creating a Windows 11 VM with Parallels Desktop
Get started using the latest Windows OS in a virtual machine on your Mac.
Installing a macOS VM on a Mac with Apple silicon
Download and install a macOS virtual machine on your Mac with Apple silicon in just a few clicks.
Cross-platform software testing and development with VMs
Learn how developers use virtual machines to develop and test applications more efficiently.
Take the next step
The Parallels ecosystem offers a variety of virtualization and virtual machine solutions, allowing you to choose the product or combination of products that best fit your needs.
For individual power users who want to create VMs on their Macs to run Windows or Linux, Parallels Desktop offers that capability plus access to over 50 productivity tools.
For organizations seeking to expand their virtualization capabilities and streamline their IT departments, Parallels RAS provides access to virtual infrastructure on a larger scale.