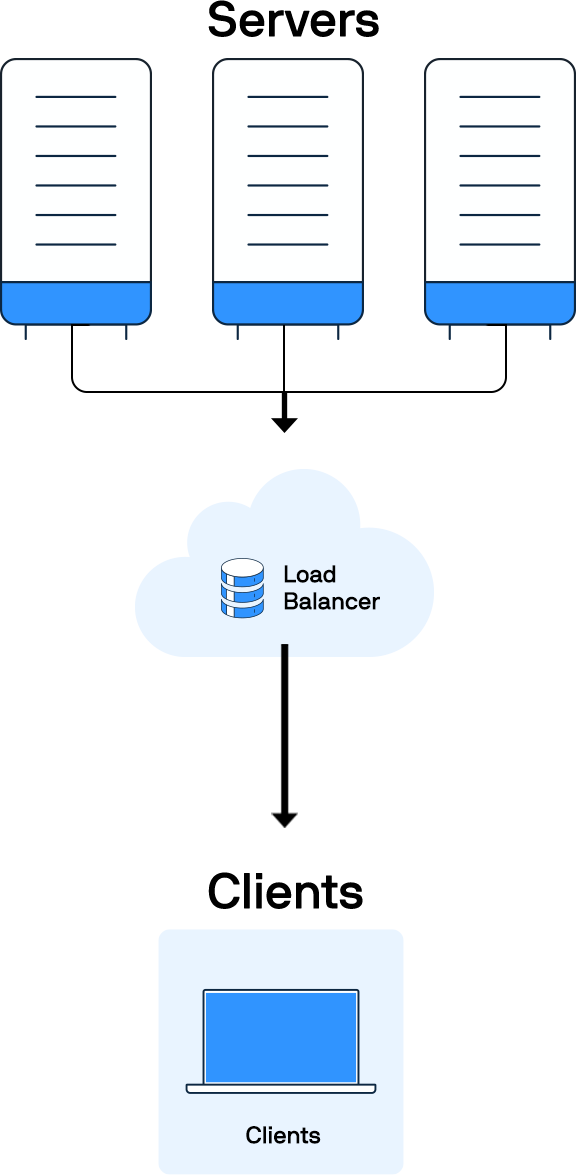
How does load balancing work?
A load balancer receives client requests and forwards them to an available server. It will typically choose a server from the available pool based on a load-balancing algorithm.
You can monitor the load balancer’s health. The balancer will not send traffic to a server that is unavailable or unhealthy. Instead, it will reroute all new requests to one of the healthy servers.
You can add servers to the pool to handle more traffic as needed.
Read on to learn the difference between public and private load balancers and more.
What are the different types of load balancers?
There are different types of load balancers that cater to various needs, from basic network traffic distribution to complex application-aware routing, enabling organizations to choose the most suitable option for their specific requirements. In a nutshell:
- Hardware load balancers: These are physical devices dedicated to distributing network traffic across multiple servers. They can handle large volumes of traffic but are often expensive and less flexible.
- Software load balancers: As the name suggests, these applications perform load balancing functions and can be installed on servers. They are more flexible and cost-effective than hardware load balancers.
- Virtual load balancers: Virtual balancers combine the software of a hardware load balancer running on a virtual machine.
- Network load balancers: These operate at the transport layer (known as layer 4) and distribute traffic based on IP protocol data. They are fast and can handle millions of requests per second.
- Application load balancers: These work at the application layer (layer 7) and can make routing decisions based on HTTP headers and other application-level data. They offer more flexibility in traffic distribution.
- Global server load balancers: These distribute traffic across geographically dispersed servers to optimize performance and availability.
- DNS load balancers: These use the Domain Name System to distribute network requests across a pool of resources.
- Cloud-based load balancers: These are offered by cloud providers as managed services, such as AWS Elastic Load Balancer.
What's the difference between public vs. private load balancers?
The main difference between public and private load balancers lies in their accessibility and the type of IP addresses they use. The choice between public and private load balancers depends on whether the application needs to be accessible from the internet or only from within a private network environment.
Public load balancers
Public load balancers have a public IP address accessible from the internet. They load and balance internet traffic to backend servers.
The cloud provider assigns these public load balancers a public IP address and uses them for applications that need to be accessible from the internet.
It's important to understand that public load balancers require public subnets and a VPC/virtual network internet gateway.
Since these load balancers are exposed to the internet, additional security measures like firewalls and network security groups are crucial.
Clients connect over the public internet using the load balancer's public IP or DNS name.
With public load balancers, you cannot specify a private subnet.
You must configure a Network Address Translation (NAT) gateway to ensure reachability between the public load balancer and its public IP address-based backends.
This gateway gives cloud resources without public IP addresses access to the internet without exposing those resources to incoming internet connections.
Private load balancers
Private (internal) load balancers have only private IP addresses accessible from within the virtual network or connected networks.
They are used to balance traffic inside a virtual network and are assigned private IP addresses from the subnet in which they are deployed.
Private load balancers differ from public load balancers because they are used for internal applications or multi-tier architectures. Backend tiers are not directly exposed to the internet and can be placed in private subnets without internet access.
These load balancers provide an additional layer of isolation from the public internet.
Some clients must be within the same virtual network or connected via a VPN/direct connection to reach the load balancer.
Two types of load balancing algorithms and the methods to deploy
There are two primary forms of algorithms when it comes to load balancing.
Those are:
- Static load balancing algorithms
- Dynamic load balancing algorithms
There are four methods to deploy load balancers.
- Hardware-based: Dedicated physical devices installed in the network.
- Software-based: Applications that run on servers, virtual machines, or the cloud.
- Cloud-based services: Load balancing features provided by cloud platforms or content delivery networks (CDNs).
- Global server load balancing (GSLB): Distributes traffic across multiple data centers or geographic regions.
When choosing a load-balancing algorithm and deployment method, consider factors like the application's requirements, server capabilities, network infrastructure, and desired level of adaptability to changing conditions.
Read on to discover the differences between dynamic and static load balancers.
Dynamic load balancing algorithms
First, it's important to note that dynamic load balancing uses algorithms that consider each server's health. Traffic is distributed accordingly.
Dynamic load balancing algorithms are different from static load balancing algorithms in the following ways:
- Least connection: This algorithm sends requests to the server with the fewest active connections. It checks which servers have the fewest connections open at the time and sends traffic to those servers. Of course, this hinges on all connections having roughly equal processing power.
- Weighted least connection: This method combines server weights with the least connection method. It allows admins to assign different weights to each server, assuming some can handle more connections than others.
- Least response time: The server or servers with the fewest active connections and fastest response times will receive most of the new traffic.
- Resource-based (adaptive): This algorithm makes decisions based on real-time server performance metrics collected by agents running on servers. The algorithm distributes the load based on the resources each server has available at the time.
Static load balancing algorithms
Static load balancing distributes traffic without making the adjustments that dynamic load balancing can make on the fly.
From round-robin style distribution to randomized distribution, traffic may be sent to servers in order or at random.
However, it does not work with real-time feedback, so users get what they get regarding wait times.
Static load balancing algorithms feature:
- Round robin: This algorithm distributes requests sequentially across servers in rotation. The algorithm distributes traffic to a list of servers using the domain name system (DNS). A nameserver will have a list of different IP addresses and provide a unique server in response to each DNS query.
- Weighted round robin: This is like Round Robin (above) but assigns weights to servers based on their capacity so that admins can assign different weights to each server. The servers that can handle more traffic will receive slightly more, and the weighting can be configured within DNS records.
- Source IP hash: This algorithm generates a hash value based on the client's IP address to determine server assignment. It combines the incoming traffic source and destination IP addresses and uses a mathematical function to convert it into a hash. Based on the hash, the connection is assigned to a specific server.
- URL hash: Creates a hash value from the request URL to assign servers. With this setup, the load balancer relies on hash data from incoming network packets, including the source and destination's Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. This option can be complicated to set up, making it more complex than the other algorithms discussed in this section.
- Randomized: This algorithm randomly distributes requests to available servers and does not consider the current load.
Load balancing with AWS
Like any other load balancer, the Amazon Web Service (AWS) Gateway Load Balancer organizes your network traffic to serve your users better and faster.
Secondary to this is that it can allow your virtual appliances to scale on demand.
So, if your organization currently uses or plans to use virtual appliances, the service is intended primarily for you.
Some examples of virtual appliances include those that strengthen your network security, including firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
The AWS Gateway Load Balancer routes traffic to the appropriate virtual appliance in your network instead of traffic going directly to virtual appliances.
With the AWS Gateway Load Balancer, traffic is routed to healthy virtual appliances and rerouted away from failing ones. It can help reduce administrative costs since traffic is centralized through the gateway.
It can also ensure that policies are enforced consistently across your appliances.
You can purchase third-party virtual appliances and solutions like this one through the AWS Marketplace.
Since any third-party virtual appliance or solution can be connected as-is to the AWS Gateway Load Balancer without altering any other endpoint, this solution is ideal for network analytics.
They allow you to quickly catch potential network issues and make your network more resilient.
Moreover, the AWS Gateway Load Balancer also works with network orchestration tools.
One such tool is AWS CloudFormation, which eases the deployment and management of AWS resources in your IT infrastructure.
Parallels RAS integrates with AWS to provide a seamless and efficient load-balancing solution for delivering applications and desktops. Here's how this integration works:
-
Setting up AWS integration with Parallels RAS:
- Administrators can add AWS as a cloud provider within the Parallels RAS Console. To do so, navigate to the "Farm" section, select "Providers," and choose Amazon Web Services from the list of available providers.
- The setup requires entering AWS credentials to deploy the Parallels RAS agent to the Amazon EC2 instances.
-
Provisioning and autoscaling:
- Parallels RAS simplifies the process of provisioning and managing Amazon EC2 instances. Administrators can create templates for RD Session Hosts, which are then cloned and managed directly from the Parallels RAS Console2.
- The system supports autoscaling to help optimize costs and ensures that resources are available when needed.
-
Load balancing:
- Parallels RAS uses built-in load balancing to distribute user sessions across multiple Amazon EC2 instances. This capability ensures that no single instance becomes a bottleneck, enhancing performance and reliability.
- The load balancing mechanism considers various factors, such as the number of active sessions and server health, ensuring efficient resource utilization.
-
User access and management:
- After setup, users can access applications and desktops through the Parallels Client or a web browser. The system detects the client type and provides the appropriate access method.
- Administrators can manage and publish resources to users, ensuring access to necessary applications and desktops from any device, anywhere.
-
Cost optimization:
- Parallels RAS includes cost-saving features, such as buffer settings, power management, and automated deletion of unused virtual machines. These settings help reduce unnecessary expenses by ensuring that only the required resources are active.
What are the benefits of load balancing?
Load balancing is a crucial technology for organizations that want to optimize their network performance, ensure high availability, and provide a better user experience. It is a key aspect of high availability or HA architecture.
The key benefits of load balancing include:
- Improved scalability: Load balancers can distribute traffic across multiple servers, enabling systems to handle sudden spikes in traffic and scale resources up or down as needed.
- Enhanced performance: By distributing workloads evenly, load balancing improves application response times and overall network performance.
- Increased reliability and uptime: Load balancers can detect server failures and automatically redirect traffic to healthy servers, reducing downtime.
- Cost efficiency: Optimizing resource utilization helps reduce operational and infrastructure costs, enhancing the total cost of ownership (TCO).
- Maintenance flexibility: Administrators can perform server maintenance without affecting overall system availability.
- Improved security: Load balancers can provide additional protection against attacks (such as DDoS attacks) by distributing malicious traffic across multiple servers. Load balancing also enables SSL passthrough for more secure data transfers.
- Better user experience: Load balancing enhances the overall user experience by ensuring smooth operation and quick response times.
- Global reach: Cloud load balancing can distribute traffic across servers in different geographic locations, reducing latency for users worldwide.
- Efficient failure management: Load balancers can quickly detect and manage failures, minimizing their impact on services.
- Predictive analysis: Some load balancers can forecast traffic patterns, allowing proactive resource management.
Here's how to deploy load balancing with Parallels RAS
To deploy load balancing with Parallels Remote Application Server (RAS), one should follow these steps:
Set up your Parallels RAS environment
Ensure that your Parallels RAS environment is appropriately set up and configured. This process includes installing Parallels RAS on your servers and configuring the necessary settings for your applications and desktops.
Configure high availability load balancing (HALB)
Parallels RAS offers high availability load balancing (HALB) to distribute traffic evenly across servers. Here's how to deploy HALB:
- Deploy HALB appliance: Each site in Parallels RAS must have at least one HALB appliance deployed. The HALB appliance acts as a load balancer within the site.
- Configure HALB: In the Parallels RAS Console, navigate to the "High Availability Load Balancing" section and configure the HALB settings, including IP addresses and the servers to be included in the load balancing pool.
Resource-based load balancing
Parallels RAS uses resource-based load balancing to dynamically distribute traffic based on various counters, such as the number of existing user sessions and server performance metrics.
- Enable resource-based load balancing: In the RAS Console, enable resource-based load balancing and configure the relevant counters and thresholds to optimize traffic distribution.
Front-end load balancing with Azure Load Balancer
Configure an Azure Load Balancer to front-end and load-balance your Parallels RAS environment.
- Deploy Azure Load Balancer: Follow Parallels' step-by-step guide to deploy and configure Azure Load Balancer. This process includes setting up the load balancer, defining the backend pool, and configuring health probes and load balancing rules.
Integration with third-party load balancers
Parallels RAS can also integrate with third-party load balancers like Kemp LoadMaster to provide resilience and scalability.
- Configure third-party load balancer: Set up the third-party load balancer to work with Parallels RAS by defining the necessary settings, such as the backend servers, health checks, and load balancing algorithms.
Testing and monitoring
- Test load balancing configuration: After setting up load balancing, perform thorough testing to ensure traffic is distributed as expected and failover mechanisms are working correctly.
- Monitor performance: Use monitoring tools provided by Parallels RAS and any integrated load balancers to monitor server performance and traffic distribution.
Parallels and load balancing
Parallels Remote Application Server (RAS) offers robust load balancing capabilities to optimize performance and ensure high availability for your IT infrastructure.
It provides built-in High Availability Load Balancing (HALB) that intelligently distributes traffic among healthy gateways and servers, eliminating single points of failure.
Parallels RAS supports both resource-based and round-robin load-balancing methods.
The resource-based approach dynamically distributes traffic based on factors like existing user sessions, memory, and CPU utilization, ensuring optimal resource allocation.
Parallels RAS integrates with third-party load balancers like AWS Elastic Load Balancer and Azure Load Balancer for added flexibility.
The platform also offers auto-scaling capabilities through RDSH templates, allowing dynamic provisioning of RDS servers based on workload thresholds.
Parallels RAS provides redundancy and failover protection, ensuring applications remain available even if individual components fail.
With its intuitive interface and out-of-the-box functionality, Parallels RAS simplifies the deployment and management of load balancing solutions. It is an ideal solution for organizations seeking to enhance performance and reliability without complex configurations or expensive add-ons.
Parallels RAS integrates seamlessly with AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) and Azure Load Balancers to enhance load distribution and ensure high availability for applications and desktops.
Resources
Take the next step
Parallels RAS is an ideal solution for load balancing, offering seamless integration with AWS Elastic Load Balancer and Azure Load Balancer to ensure optimal performance.
It dynamically distributes traffic across servers based on real-time metrics, maximizing resource utilization and minimizing downtime, all without the need for complex configurations or costly add-ons.
Ready to take the next step and optimize your load balancing with Parallels RAS?






