The best way to run Windows on Mac: Why Parallels Desktop is a great VirtualBox alternative
Can’t decide what’s a better fit for your needs, Parallels Desktop vs. VirtualBox? Or just trying to find a good alternative to VirtualBox?
Discover how Parallels Desktop is a superior way to run Windows or Linux on Mac, seamlessly creating virtual machines on Apple M series Macs and more.
14-day fully functional free trial
Why choose Parallels Desktop as your virtualization solution?
See why real-world users prefer Parallels Desktop to VirtualBox
Many individual users, teams, businesses, and organizations prefer Parallels Desktop over VirtualBox, and you don’t have to take our word for it! Discover how real users benefit from using Parallels Desktop.
"I use Parallels Desktop to access Windows on my Mac. There are eLearning, and local government design applications that require the exclusive use of the Windows OS, and this has helped me not to need to have two computers but to work on one machine with access to both operating systems. Additionally, on occasion, there are colleagues who require support on their computers, and I can replicate the problem they may have with the operating system they are running in a friendly and very fast way."
"Parallels Desktop is used in my organization and with our customers to support Windows apps when there is no Mac application, or the Mac Application is not fully featured.
We have a legacy application where only administrative functions can be performed in a Windows App. For some of our customers, all users are Mac users. Parallels and their Coherence Mode provide these users with a near-seamless virtual machine/desktop experience. Coherence Mode means they don't have to deal with a Windows environment and can work side-by-side with our app and their other Mac apps (Adobe Creative Cloud apps, for example)."
"We are an all-Apple environment, but still, we have plenty of applications that require us to run Windows. In some cases, we have entire departments with this need; in other instances, it’s a single user. Before implementing Parallels Desktop, we had some people who were lugging around an old Dell laptop in addition to a MacBook Pro for a single application. The IT department also uses [Parallels Desktop] to easily spin up virtual machines for testing and training on our machines."
14-day fully functional free trial
Discover how Parallels Desktop is the right VirtualBox alternative for both users and organizations
A seamless experience
Run the full-featured version of Windows applications on your Mac, including the most popular Windows apps like Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook to PC-exclusive games.
Effortlessly meet your professional and educational application needs with just one new piece of software — Parallels Desktop.
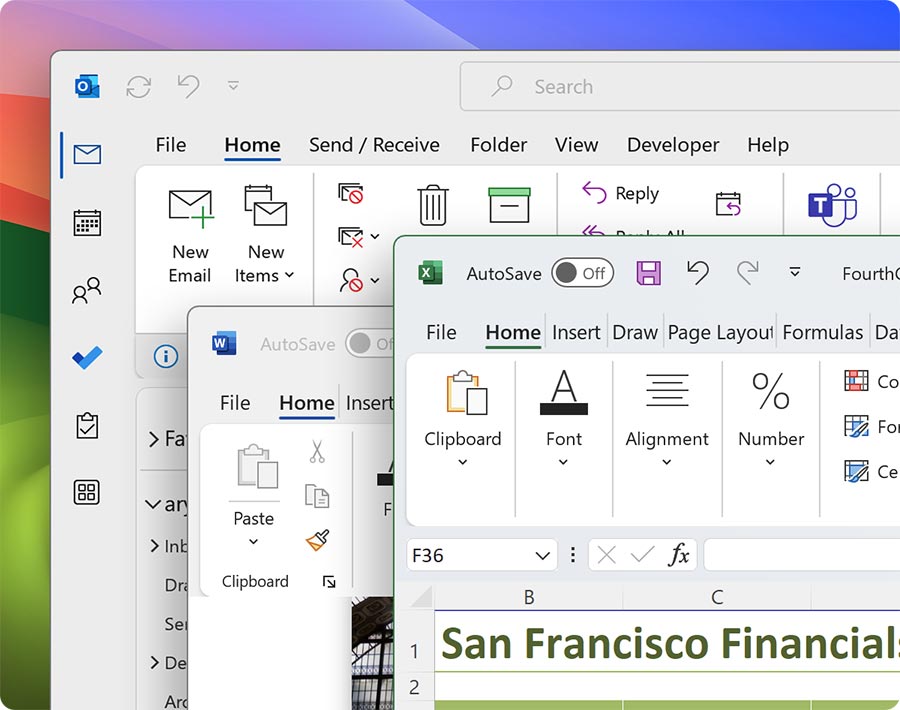
Enjoy your hardware of choice
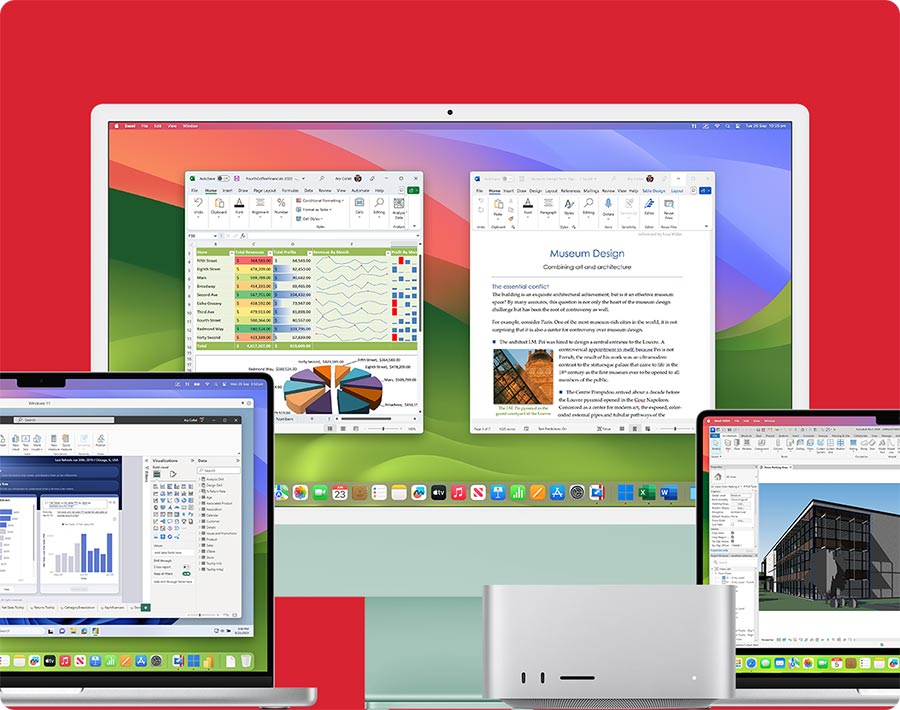
Run all the apps you need for work, school, and entertainment, including full-featured Microsoft Office 365 applications, accounting software, trading software, AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and more on your Mac.
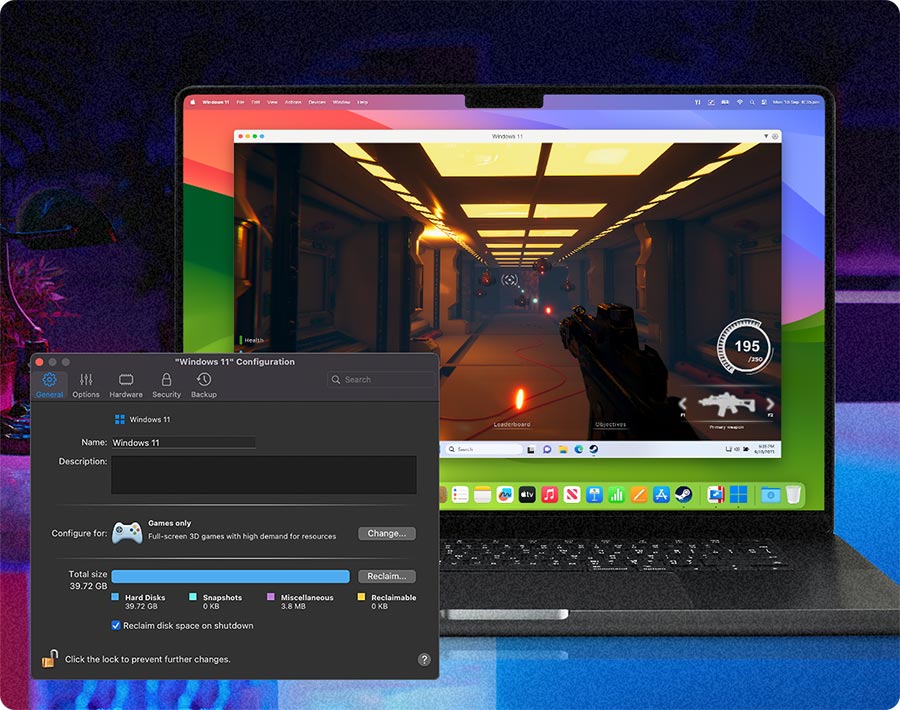
Run your favorite PC games on a Mac
Play hundreds of Windows-exclusive games on Mac with Parallels Desktop, from first person to multiplayer games. Parallels Desktop transforms your Mac into a gaming machine.
World-class technical support
Need assistance? Parallels Desktop subscribers get access to online customer support, detailed documentation, and an active community contributing to a rich knowledge base. Find answers to all your questions and become a Parallels Desktop power user.
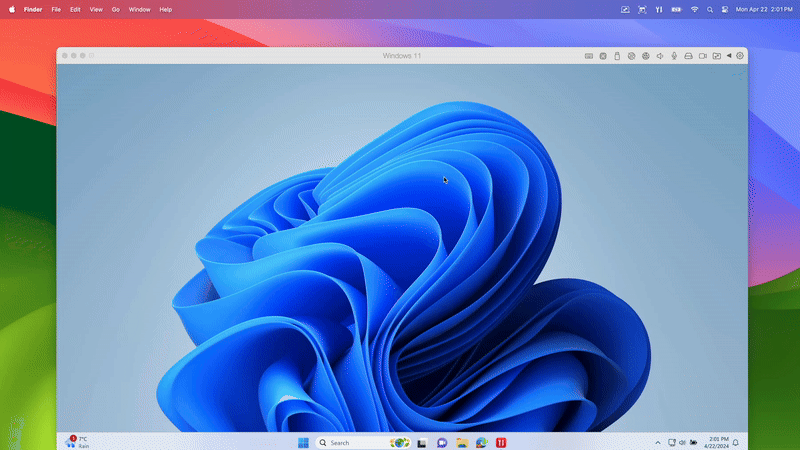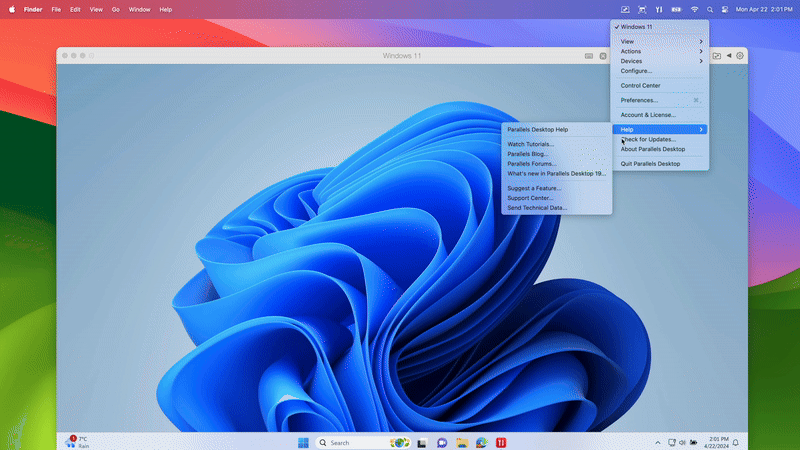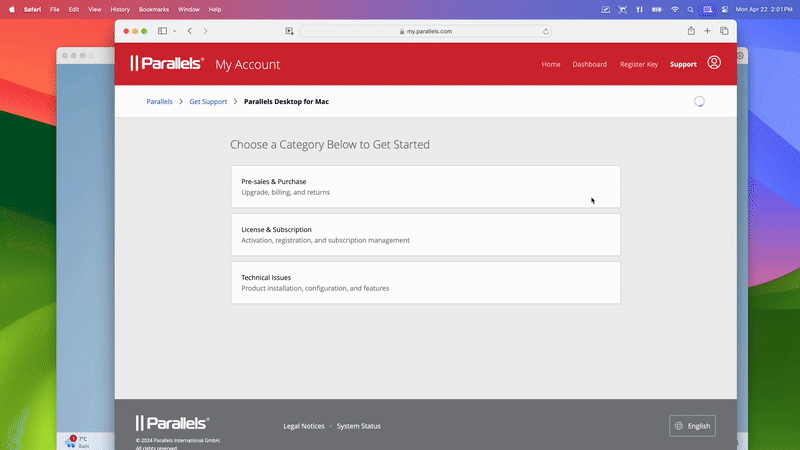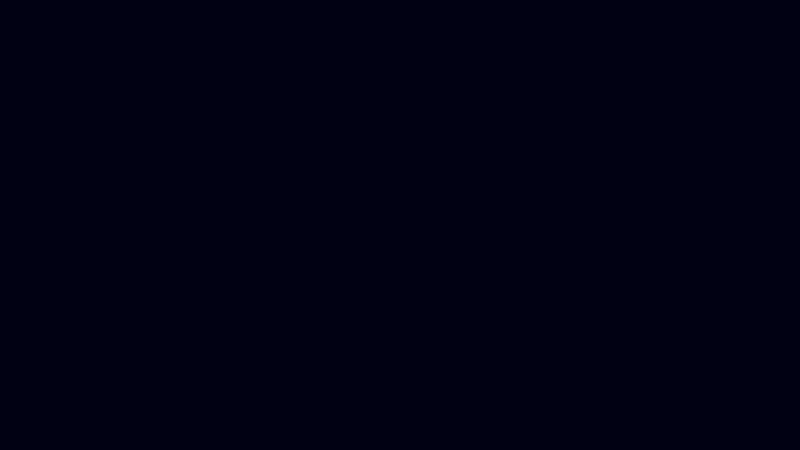
Get started with Parallels Desktop and maximize the potential of your Mac
Here’s how to migrate from VirtualBox to Parallels Desktop
Open Parallels Desktop
Open Parallels Desktop and select File > Open on the menu bar.
Import
Select the Windows data file you want to import, then click Open.
Migrate to VirtualBox
After you start Windows, select Actions > Install Parallels Tools and follow the onscreen instructions. For more information on how to migrate VirtualBox virtual machines to Parallels Desktop, explore this Knowledge Base article.
Parallels Desktop is solution you need for many use cases...
Cross-platform development and testing
Build, test, and QA your code in all necessary platforms seamlessly in a virtual environment. Developers and testers, switch between operating systems and browsers effortlessly, maintaining high performance, isolation, and security. Streamline the development process and reduce risk with Rollback mode, a Microsoft Visual Studio plug-in, and more.
Fulfill educational demands
Educators and students need cross-platform compatibility to learn. Meet academic requirements and access the essential tools for your studies or career, including the full-featured Windows version of Microsoft Office 365, Windows-based CAD tools, common statistics and accounting software, and more.
Compatible with Office 365 applications
Experience a Windows OS environment on your Mac. Use a virtual machine to run the full-featured versions of the most commonly used Office 365 applications, including Microsoft Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook.
14-day fully functional free trial
Parallels Desktop vs. VirtualBox FAQs
Converting your VirtualBox virtual machine to a Parallels Desktop one is fast and easy. Note that due to architecture differences, you cannot currently convert a VirtualBox virtual machine from an Intel-based Mac to a Mac with an Apple M-series chip.
It just takes four simple steps! Follow these instructions to get started migrating your VirtualBox machine to Parallels Desktop:
- Open Parallels Desktop and select File > Open on the menu bar.
- Select the Windows data file you want to import, then click Open.
- Start Windows.
- Select Actions > Install Parallels Tools and follow the onscreen instructions.
Before beginning the migration, make sure you have deleted previous tools from your virtual machine and fully shut it down prior to migration (do not suspend or hibernate the virtual machine).
And that’s it! You’ve converted your VirtualBox VM to a Parallels Desktop VM.
Yes, some users have noted that VirtualBox uses more RAM on the host system than allocated for the virtual machine.
Parallels Desktop offers customer support across various channels, including phone, email, and live chat, for the lifetime of your subscription. VirtualBox is an open-source product, so users must rely on community support, forums, and crowdsourced documentation for troubleshooting.
Parallels Desktop offers an easy setup and integration with macOS, making it simple for less technical users to install and use. VirtualBox does offer community-based support and extensive documentation but requires more technical knowledge.
Parallels Desktop offers more support for DirectX, which is necessary for running Windows games or applications that require 3D acceleration on Macs with Intel or Apple silicon. VirtualBox only offers limited DirectX support, which may limit its capacity for high-end gaming or more advanced 3D applications.
Is VirtualBox not the solution for you? Choose the right Parallels Desktop version for your needs and enjoy a better VirtualBox alternative
Standard Edition
Limited version for those that need to run Windows applications on base model Mac computers.
Supports future operating systems.
Current version only. Full compatibility with future versions not guaranteed.
Pro Edition
Versatile, fully loaded version for developers, individual business users, and gamers seeking the best performance and productivity.
Supports future operating systems.





