Instead of relying on traditional network boundaries, ZTNA evaluates contextual signals like device health, user role, geolocation, and access behavior. Only the minimum level of access is granted, and it's dynamically adjusted based on ongoing risk assessments.
How does Zero Trust architecture work?
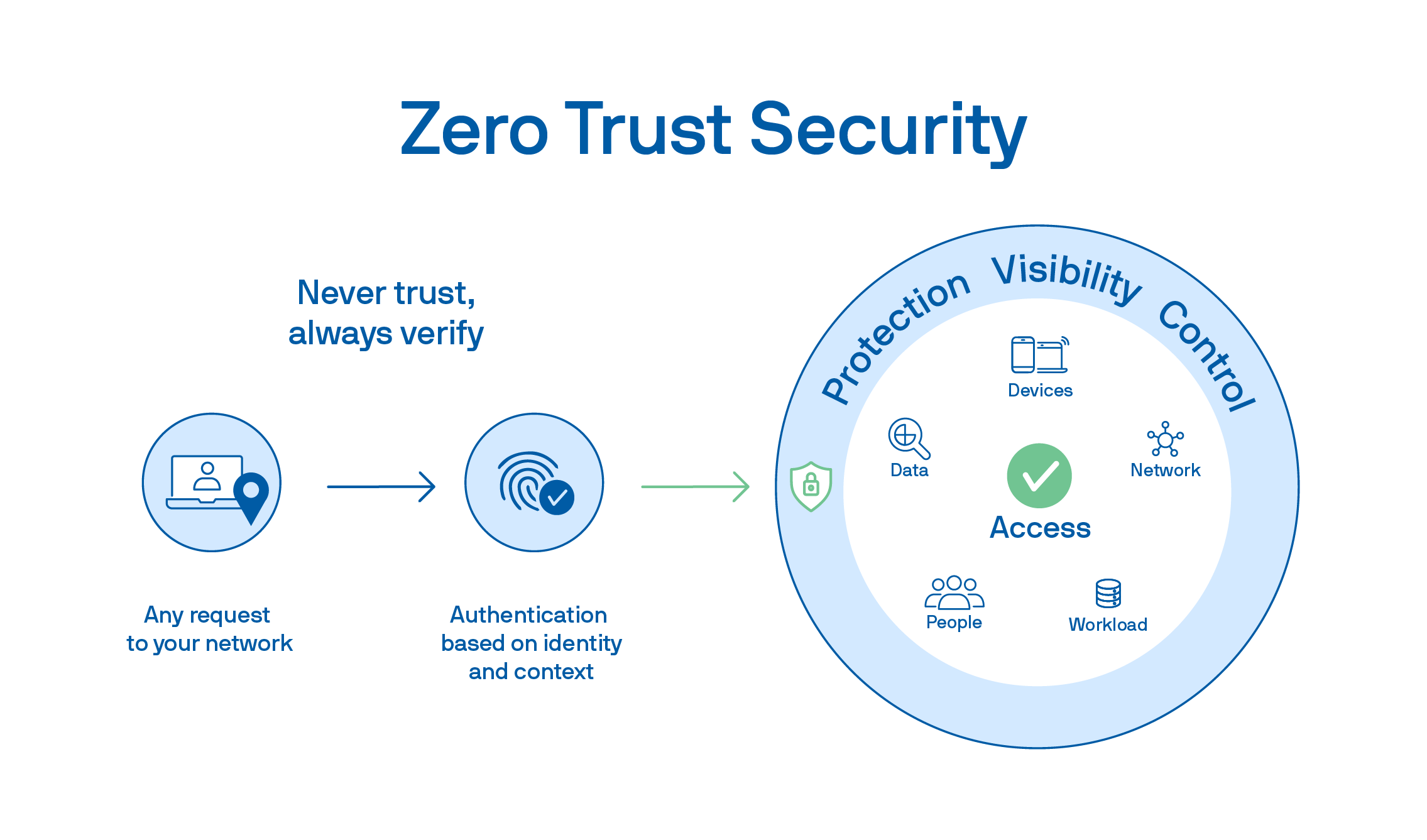
The Zero Trust network architecture definition centers on a shift in mindset—assuming every request is untrusted by default and flipping the old model on its head.
Instead of assuming everything inside the network is safe, it treats every request, whether from inside or outside, as suspicious until proven otherwise.
Let’s say a remote employee tries to initiate a session through Zero Trust network access to reach a cloud app.
ZTNA checks who they are, what device they're using, where they are, and whether it all adds up.
Only then is access granted, and even then, it's limited to exactly what they need. Nothing more.
What methods or techniques are involved in Zero Trust network architecture?
ZTNA isn't one tool but rather a security strategy guided by a Zero Trust policy, supported by a range of tightly coordinated security tactics:
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
One of the methods of ZTNA is multi-factor authentication, which adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity using two or more factors, such as a password, a device, or a fingerprint, before gaining access.
Endpoint verification
ZTNA checks the security posture of each device before granting access, ensuring it's authorized, up to date, and free from threats.
If the device doesn’t meet requirements, access is denied.
Micro-segmentation
Think of your network as rooms in a house. Through micro-segmentation, ZTNA locks each door, so users only get into the rooms they need.
Context-based access policies
Context-based access policies consider more than just who you are—they also take into account where you're connecting from, when, and on what device.
These policies add an extra layer of security by adapting to changing risk factors in real time.
Continuous authentication
With Zero Trust, it's not one-and-done.
The authentication of requests is continuous to uphold security all the time.
Even after logging in, ZTNA watches for unusual behavior and can revoke access in real time.
Real-time threat identification
ZTNA actively hunts for threats, flagging anything suspicious and stopping it before damage is done.
Underlying architecture
ZTNA is built on software-defined perimeters and policy engines that dynamically allow or block traffic.
In-line approach
Every request is inspected in real time before reaching its destination, ensuring consistent policy enforcement.
Nothing gets through without being checked for identity, device health, and compliance.
Environment-agnostic security
Whether it's cloud architecture, on-premises or hybrid, ZTNA applies the same rules everywhere.
What are the best practices of Zero Trust network architecture?
Zero Trust works best when it's intentional and thorough. These practices help make it stick:
Identity and access management (IAM)
You can't protect what you don't control. IAM centralizes identity checks and enforces who gets in and what they can see.
Device access control
Only secure, verified devices are allowed in. This stops rogue devices before they become a problem.
Least privilege access
With least privilege access, users only get access to what they need—nothing more, nothing less.
Network segmentation
Dividing the network into zones limits the blast radius if something goes wrong.
Continuous monitoring
Stay ahead of threats and performance issues with around-the-clock visibility into user behavior, connection quality, and system activity.
With continuous monitoring anomalies are detected early, enabling fast, informed responses to maintain security and productivity.
Principles of Zero Trust
-
Never trust, always verify. Every request is suspicious until proven safe.
-
Assume breach. Work like an attacker is already inside, and limit what they can access.
-
Limit access. Users and devices only get what they need, nothing more.
-
Inspect everything. All traffic is monitored—internal, external, east-west, you name it.
-
Adapt in real-time. Use context (like location and behavior) to update permissions on the fly.
See how Parallels Browser Isolation enables you to set up a Zero Trust network architecture in your organization.
What are the benefits of Zero Trust network architecture?
As the way we work becomes more remote and cloud-based, a Zero Trust model is one of the best ways to keep your organization safe. Here’s why:
Reduces the attack surface. Micro-segmentation and strict access rules make it harder for attackers to move laterally.
Protects sensitive data. Whether it's in the cloud or on-prem, data access is tightly controlled and monitored.
Boosts visibility. ZTNA gives IT teams a clear view of who's accessing what and from where.
Improves compliance. With built-in logging and access policies, audits become easier.
Enables secure remote work. No more worrying about insecure Wi-Fi or rogue devices. ZTNA has it all covered.
What are some use cases for Zero Trust network architecture?
Zero Trust network architecture supports a wide range of modern business needs. From securing remote teams to protecting cloud-based resources, here are some common use cases:
Hybrid and remote working
With employees scattered across homes, offices, and coffee shops, ZTNA ensures secure access no matter where they log in.
Cloud migration
ZTNA makes moving to the cloud safer. As resources shift out of the data center, Zero Trust ensures only the right people get in.
Mobile working
ZTNA empowers employees to work securely from any device, smartphone, tablet, or laptop, without compromising speed or user experience.
It ensures smooth access to corporate resources while keeping data protected, enabling true business mobility.
How do organizations implement Zero Trust network architecture with Parallels Workspace solutions?
Regione Autonoma Friuli Venezia Giulia adopted Parallels RAS to enable secure remote work for over 2,000 public sector employees while embracing a Zero Trust approach. With built-in multilevel authentication, encryption, and centralized management, Parallels RAS ensures that only verified users can access sensitive government and healthcare systems.
Farmers & Merchants Bank relies on Parallels RAS to deliver secure, low-latency remote access while aligning with Zero Trust principles. By replacing legacy VPN and VDI solutions, the bank gained granular control over user access—especially for third-party auditors and consultants—limiting exposure to only necessary applications.
ACE Technology Group leverages Parallels RAS to deliver secure, affordable remote desktop solutions that align with Zero Trust principles. As a managed IT provider for SMBs, ACE uses the platform’s granular access controls, FIPS 140-2 encryption, and centralized management to ensure secure access without overburdening clients or their own team. The usage-based licensing model simplifies operations, cuts costs, and allows for rapid scaling, crucial during disaster recovery scenarios like Hurricane Ida.
Parallels and Zero Trust network architecture
Parallels solutions are purpose-built to support Zero Trust network architecture. From identity-based access to real-time monitoring and environment-agnostic deployment, Parallels RAS gives IT teams the tools to implement ZTNA without complexity or compromise.
Resources
Explore how Zero Trust has evolved and how organizations can practically adopt it to strengthen remote work security.
Key strategies for integrating Zero Trust into cloud architecture
Uncover five powerful strategies to embed Zero Trust into your cloud infrastructure—fortifying security, simplifying IT operations, and delivering an improved user experience.
What’s new in Parallels Remote Application Server (RAS) 20.0
Parallels RAS continues to evolve with powerful features that boost flexibility, scalability, and user experience. Recent updates include Local App Launch for faster application access, expanded support for AWS Availability Zones, enhanced integration with Windows 365, flexible Azure Marketplace licensing, and a refined remote experience across all platforms.
Take the next step
The Parallels ecosystem provides a range of cybersecurity solutions, allowing you to select the product or combination of products that best suit your neds.
Parallels RAS strengthens your cybersecurity posture by enforcing key Zero Trust principles like strict access controls and multi-factor authentication.