PARALLELS RAS USE CASES
Flexible Cloud Deployment Models with Parallels RAS
- Leverage different approaches while reducing the total cost of ownership (TCO).
- Mix and match different workloads such as Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH), virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), hypervisors, hyperconverged infrastructures and cloud providers.
- Parallels® Remote Application Server (RAS) integrates with Azure Virtual Desktop to manage and unify all virtual workloads from a centralized console, including Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session.
- Easily meet business requirements with infrastructure auto-scaling and workforce mobility.
What is On-Premises (Private Cloud) Deployment?
Businesses using a private cloud operate their own cloud computing infrastructure. They often choose a private cloud to leverage their own security protocol and/or existing infrastructure. Users then access computing resources on-demand over that private network.
Advantages
With a private cloud model, businesses have direct control over their data which helps to meet security, regulatory compliance and business governance requirements. Moreover, IT teams have full control of maintenance and upgrades.
On-Premises Deployment (Private Cloud) with Parallels RAS
Parallels RAS on-premises deployments are rolled out on either physical servers or virtual machines (VMs). This scenario applies to organizations that require end-to-end control for data, provisioning, backup and failover. In most cases, this type of setup is done in an organization’s own datacenters and sometimes with third-party providers (like colocation and regional vendors).
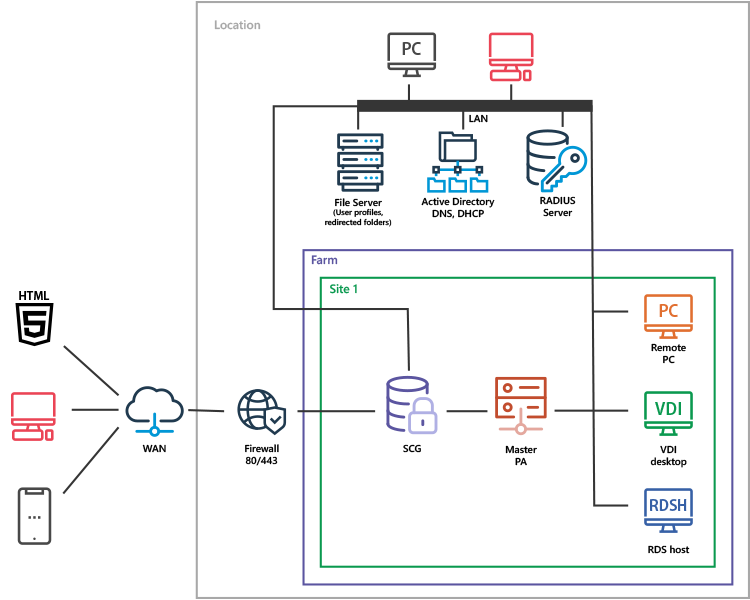
On-Premises Deployment
Parallels RAS Reference Architecture
DownloadWhat is Public Cloud Deployment?
The most common type of cloud computing deployment are public clouds. Cloud resources, such as servers and storage, are owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers and delivered over the internet. Hardware, application infrastructure and other services available off-the-shelf are managed and owned by the cloud provider. Examples of public cloud providers include Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Advantages
Public cloud deployments are highly scalable, flexible and location independent. Organizations can save money due to the drastic reduction of upfront investment, which lowers barriers to entry into the public cloud space. The readily available infrastructure of a public cloud environment enables faster access and best delivery of service for users. Additionally, the pay-as-you-go model enables organizations to be charged based on usage, thereby reducing expenses as well.
Public Cloud Deployment with Parallels RAS
Parallels RAS simplifies and enhances the delivery of virtual apps and desktops in public cloud services such as Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS). With built-in auto-scaling and load balancing capabilities, Parallels RAS utilizes and maximizes the benefits of the public cloud while providing high availability and business continuity. Parallels RAS also deploys, supports and maintains Desktop as a Service (DaaS) offerings, such as Azure Virtual Desktop.
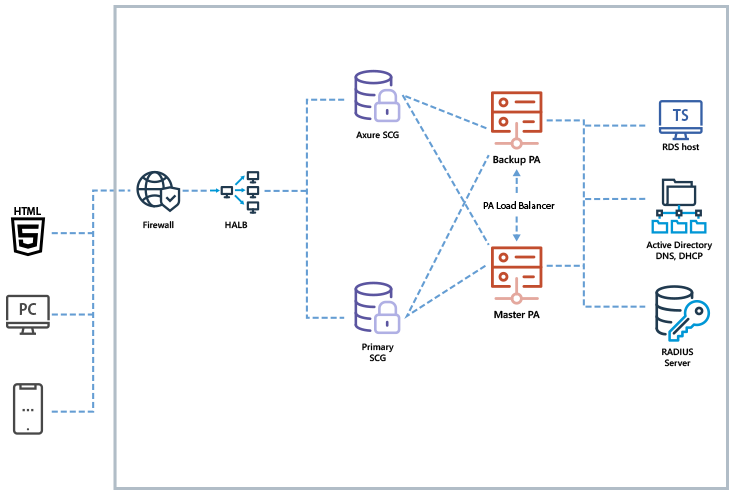
Deployment on Azure
Cloud deployments can auto-scale based on user workloads. To expand your operations in another geographical location, deploy new infrastructure. Due to the cloud’s global presence, users can access applications and desktops with a consistent experience on any device.
By deploying Parallels RAS on public clouds, organizations can use out-of-the-box high availability and advanced services such as disaster recovery.
Parallels RAS and Azure Reference Architecture
DownloadWhat is Hybrid Cloud Deployment?
Hybrid cloud models are a mix of public and private cloud workloads. Hybrid clouds enable access to applications and data residing in the two environments. Many organizations favor a hybrid cloud approach as it provides greater flexibility, compliance, security, increased deployment options and better value from existing infrastructures. Hybrid cloud enables businesses, including public sector IT solutions, to scale up on-premises infrastructures to the public cloud when necessary. Organizations may run certain workloads in the cloud but keep sensitive data in their own datacenter to meet regulatory requirements.
Advantages
The benefits of using a hybrid cloud model include its flexibility, security, adherence to compliance regulations, scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Hybrid Cloud Deployment with Parallels RAS
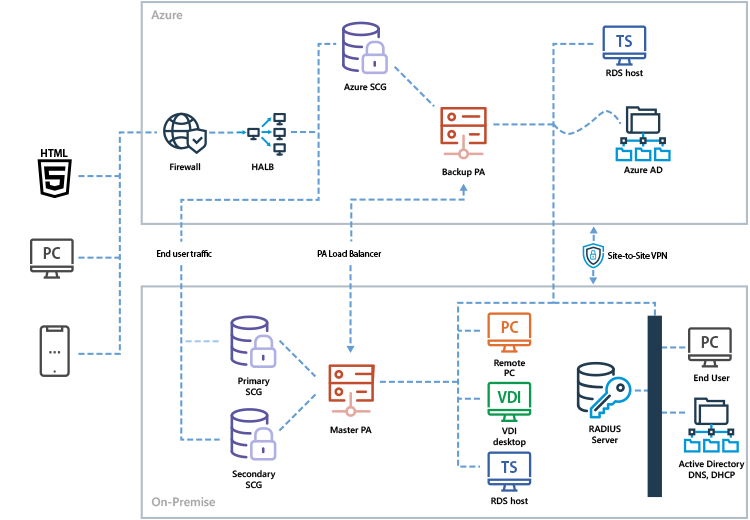
Parallels RAS supports hybrid deployment, which enables workload distribution and failover. A hybrid cloud provides flexibility when computing requirements and costs change by distributing workloads between a private and public cloud. With Parallels RAS, different scenarios can be easily implemented, from adding RD Session Hosts and handling extra end users, to having a cost-effective, high-availability infrastructure. With Parallels RAS it's possible to utilize cloud services such as Azure Virtual Desktop with session hosts on Microsoft Azure, along with other multi-session hosts such as RD Session Hosts or single session hosts such as VDI on-premises.
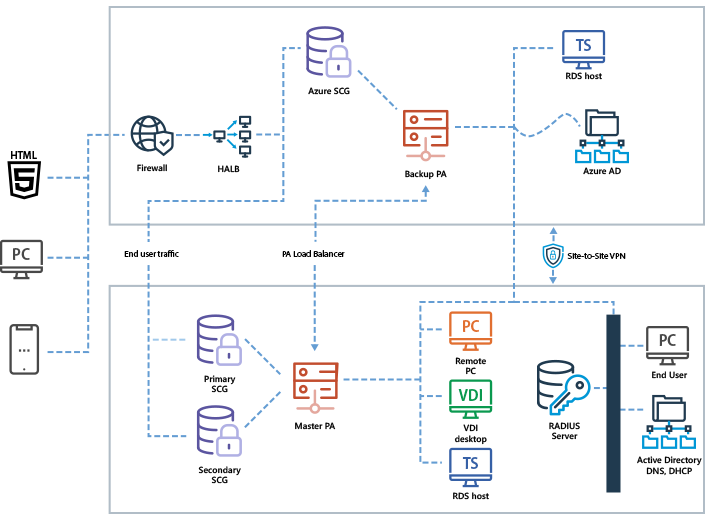
Deployment on AWS
Organizations implement a hybrid deployment to create a failover infrastructure that combines on-premises and public cloud installations. Also, a hybrid deployment can be the first step in a long-term strategy for a full transition to the public cloud.
Parallels RAS supports hybrid deployment with Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, and more cloud providers.
Parallels RAS on AWS
DownloadWhat is Hyperconverged Deployment?
Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) is a software-defined infrastructure that unifies and combines all the traditional data center elements, including storage, networking, compute, and management. The centralization of infrastructure management simplifies the deployment and scalability of hypervisors and VMs. Hyperconvergence enables organizations to deploy applications in a shared resource pool, leading to better performance.
Advantages
The benefits of using an HCI infrastructure include straightforward management, simple deployment, scalability and lower costs when compared with traditional data center architectures.
Hyperconverged Deployment with Parallels RAS
Parallels RAS is designed with hyper-converged technology in mind - it automatically generates and deploys VDI desktops on demand, enabling administrators to create and deploy guest VMs on the fly. It’s possible to create a master virtual desktop as a template and rapidly clone hundreds of virtual desktops. Parallels RAS is partners with Nutanix supporting AHV, HPE hyperconverged solutions and Scale computing on HC3, simplifying deployments, increasing flexibility and lowering costs. While hyperconverged solutions integrate datacenter resources, Parallels RAS monitors and applications and desktops from a centralized console.
Deployment on Nutanix
With HCI solutions, power and space requirements are reduced and storage complexities are eliminated. One of the main advantages of HCI is the ability to plug and play into a datacenter pool and operate instantly without further configurations.
Nutanix with VMware ESX
Download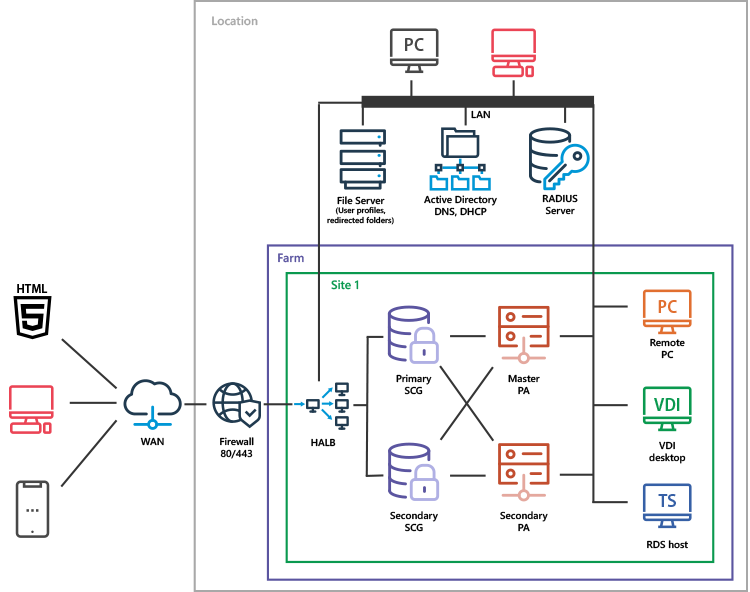
Deployment on HPE Hyper Converged
Parallels RAS delivers applications and desktops from HCI through a single and intuitive console that centralizes the management of datacenter resources.
HPE Hyper Converged
Download
Deployment on Scale Computing’s HC3
Parallels RAS supports Scale Computing’s HC3, a hyperconverged solution that combines compute, storage, virtualization, backup, and disaster recovery in a single appliance. This capability allows IT administrators to manage (start/stop/suspend/reset/delete/clone) VMs through Scale Computing HC3 API.





